The neonatal Fc receptor, FcRn, as a target for drug delivery and therapy
- PMID: 25703189
- PMCID: PMC4544678
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.02.005
The neonatal Fc receptor, FcRn, as a target for drug delivery and therapy
Abstract
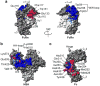
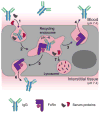
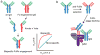
Immunoglobulin G (IgG)-based drugs are arguably the most successful class of protein therapeutics due in part to their remarkably long blood circulation. This arises from IgG interaction with the neonatal Fc receptor, FcRn. FcRn is the central regulator of IgG and albumin homeostasis throughout life and is increasingly being recognized as an important player in autoimmune disease, mucosal immunity, and tumor immune surveillance. Various engineering approaches that hijack or disrupt the FcRn-mediated transport pathway have been devised to develop long-lasting and non-invasive protein therapeutics, protein subunit vaccines, and therapeutics for treatment of autoimmune and infectious disease. In this review, we highlight the diverse biological functions of FcRn, emerging therapeutic opportunities, as well as the associated challenges of targeting FcRn for drug delivery and disease therapy.
Keywords: Albumin; FcRn; Immunoglobulin G; Nanoparticle; Protein engineering.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
J.S. and F.C.S. declare no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
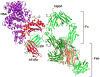
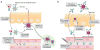


Similar articles
-
Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn): a novel target for therapeutic antibodies and antibody engineering.J Drug Target. 2014 May;22(4):269-78. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2013.875030. Epub 2014 Jan 9. J Drug Target. 2014. PMID: 24404896 Review.
-
Qualification of a homogeneous cell-based neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) binding assay and its application to studies on Fc functionality of IgG-based therapeutics.J Immunol Methods. 2013 Apr 30;390(1-2):81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2013.01.011. Epub 2013 Feb 4. J Immunol Methods. 2013. PMID: 23384837
-
The role of immunoglobulin transport receptor, neonatal Fc receptor in mucosal infection and immunity and therapeutic intervention.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Sep 10;138:112583. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112583. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38971109 Review.
-
The Neonatal Fc Receptor (FcRn): A Misnomer?Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 10;10:1540. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01540. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31354709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FcRn inhibitors: Transformative advances and significant impacts on IgG-mediated autoimmune diseases.Autoimmun Rev. 2025 Feb 28;24(3):103719. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103719. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Autoimmun Rev. 2025. PMID: 39672251 Review.
Cited by
-
Intravenous injection of a novel viral immunotherapy encoding human interleukin-7 in nonhuman primates is safe and increases absolute lymphocyte count.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Nov 30;18(6):2133914. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2133914. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 36315906 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) to treat autoimmune diseases and maternal-fetal immune cytopenias.Transfusion. 2021 May;61(5):1350-1354. doi: 10.1111/trf.16341. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Transfusion. 2021. PMID: 33650699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Glycosylation and Species Origin on the Uptake and Permeation of IgGs through the Nasal Airway Mucosa.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Oct 23;12(11):1014. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12111014. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33114132 Free PMC article.
-
FcRn-Driven Nanoengineered Mucosal Vaccine with Multi-Epitope Fusion Induces Robust Dual Immunity and Long-Term Protection Against Brucella.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 May 26;13(6):567. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13060567. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573898 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-CTLA-4 nanobody as a promising approach in cancer immunotherapy.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jan 8;15(1):17. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06391-x. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38191571 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

