B cells and antibodies in the defense against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- PMID: 25703559
- PMCID: PMC4629253
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.12276
B cells and antibodies in the defense against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
Abstract
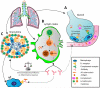
Better understanding of the immunological components and their interactions necessary to prevent or control Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection in humans is critical for tuberculosis (TB) vaccine development strategies. Although the contributory role of humoral immunity in the protection against Mtb infection and disease is less defined than the role of T cells, it has been well-established for many other intracellular pathogens. Here we update and discuss the increasing evidence and the mechanisms of B cells and antibodies in the defense against Mtb infection. We posit that B cells and antibodies have a variety of potential protective roles at each stage of Mtb infection and postulate that such roles should be considered in the development strategies for TB vaccines and other immune-based interventions.
Keywords: B lymphocytes; antibodies; immunity; immunoglobulins; tuberculosis.
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global tuberculosis report 2014. Geneva, Switzerland: 2014. http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/
-
- Colditz GA, et al. Efficacy of BCG vaccine in the prevention of tuberculosis. Meta-analysis of the published literature. Jama. 1994;271:698–702. - PubMed
-
- Trunz BB, Fine P, Dye C. Effect of BCG vaccination on childhood tuberculous meningitis and miliary tuberculosis worldwide: a meta-analysis and assessment of cost-effectiveness. Lancet. 2006;367:1173–1180. - PubMed
-
- Rook GA, Hernandez-Pando R. The pathogenesis of tuberculosis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1996;50:259–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI096213/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI063537/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-096213/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI105684/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI051519/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI-094745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-51519/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI094745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL-059842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI-063537/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-033774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI052733/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1U18 FD004012/01/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001073/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U18 FD004012/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- R37 AI033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-052733/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

