The life cycle of lipid droplets
- PMID: 25703629
- PMCID: PMC4380764
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2015.02.002
The life cycle of lipid droplets
Abstract
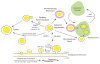
Proteomic studies have revealed many potential functions of cytoplasmic lipid droplets, and recent activity has confirmed that these bona fide organelles are central not only for lipid storage and metabolism, but for development, immunity, and pathogenesis by several microbes. There has been a burst of recent activity on the assembly, maintenance and turnover of lipid droplets that reveals fresh insights. This review summarizes several novel findings in initiation of lipid droplet assembly, protein targeting, droplet fusion, and turnover of droplets through lipophagy.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Scherer PE. Adipose tissue: from lipid storage compartment to endocrine organ. Diabetes. 2006;55:1537–1545. - PubMed
-
- Bartz R, Li WH, Venables B, Zehmer JK, Roth MR, Welti R, Anderson RG, Liu P, Chapman KD. Lipidomics reveals that adiposomes store ether lipids and mediate phospholipid traffic. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:837–847. - PubMed
-
- Bozza PT, Viola JP. Lipid droplets in inflammation and cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2010;82:243–250. - PubMed
-
- Kohlwein SD. Obese and anorexic yeasts: experimental models to understand the metabolic syndrome and lipotoxicity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1801:222–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

