Acetyl-CoA and the regulation of metabolism: mechanisms and consequences
- PMID: 25703630
- PMCID: PMC4380630
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2015.02.003
Acetyl-CoA and the regulation of metabolism: mechanisms and consequences
Abstract
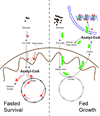
Acetyl-CoA represents a key node in metabolism due to its intersection with many metabolic pathways and transformations. Emerging evidence reveals that cells monitor the levels of acetyl-CoA as a key indicator of their metabolic state, through distinctive protein acetylation modifications dependent on this metabolite. We offer the following conceptual model for understanding the role of this sentinel metabolite in metabolic regulation. High nucleocytosolic acetyl-CoA amounts are a signature of a 'growth' or 'fed' state and promote its utilization for lipid synthesis and histone acetylation. In contrast, under 'survival' or 'fasted' states, acetyl-CoA is preferentially directed into the mitochondria to promote mitochondrial-dependent activities such as the synthesis of ATP and ketone bodies. Fluctuations in acetyl-CoA within these subcellular compartments enable the substrate-level regulation of acetylation modifications, but also necessitate the function of sirtuin deacetylases to catalyze removal of spontaneous modifications that might be unintended. Thus, understanding the sources, fates, and consequences of acetyl-CoA as a carrier of two-carbon units has started to reveal its underappreciated but profound influence on the regulation of numerous life processes.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrated Analysis of Acetyl-CoA and Histone Modification via Mass Spectrometry to Investigate Metabolically Driven Acetylation.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1928:125-147. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9027-6_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30725455 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose starvation induces a switch in the histone acetylome for activation of gluconeogenic and fat metabolism genes.Mol Cell. 2022 Jan 6;82(1):60-74.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.12.015. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 34995509 Free PMC article.
-
Acetyl-CoA regulates lipid metabolism and histone acetylation modification in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023 Jan;1878(1):188837. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188837. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36403921 Review.
-
The protein acetylome and the regulation of metabolism.Trends Plant Sci. 2012 Jul;17(7):423-30. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.03.008. Epub 2012 Apr 13. Trends Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22503580 Review.
-
Crosstalk between cellular metabolism and histone acetylation.Methods Enzymol. 2019;626:1-21. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2019.07.013. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Methods Enzymol. 2019. PMID: 31606071
Cited by
-
The Potential Mediation of the Effects of Physical Activity on Cognitive Function by the Gut Microbiome.Geriatrics (Basel). 2020 Sep 25;5(4):63. doi: 10.3390/geriatrics5040063. Geriatrics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32992812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences of Pine Wood Nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus) Developmental Stages under High-Osmotic-Pressure Stress.Biology (Basel). 2024 Feb 16;13(2):123. doi: 10.3390/biology13020123. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392341 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial quality control in health and cardiovascular diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Nov 6;11:1290046. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1290046. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38020895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteria employ lysine acetylation of transcriptional regulators to adapt gene expression to cellular metabolism.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 23;15(1):1674. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46039-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38395951 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Sweet Secrets of HCC: Glucometabolic Rewiring in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338231219434. doi: 10.1177/15330338231219434. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 38083797 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

