Non-traditional cytokines: How catecholamines and adipokines influence macrophages in immunity, metabolism and the central nervous system
- PMID: 25703786
- PMCID: PMC4590987
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.01.008
Non-traditional cytokines: How catecholamines and adipokines influence macrophages in immunity, metabolism and the central nervous system
Abstract
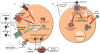
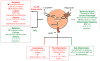
Catecholamines and adipokines function as hormones; catecholamines as neurotransmitters in the sympathetic nervous system, and adipokines as mediators of metabolic processes. It has become increasingly clear, however, that both also function as immunomodulators of innate and adaptive immune cells, including macrophages. Macrophages can respond to, as well as produce their own catecholamines. Dopamine, noradrenaline, and adrenaline are the most abundant catecholamines in the body, and can induce both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory immune responses in macrophages, as well as non-immune processes such as thermogenesis. Though they are responsive to adipokines, particularly lipoproteins, leptin, and adiponectin, macrophages generally do not synthesize their own adipokines, with the exception being resistin-like molecules. Adipokines contribute to adverse metabolic and immune responses by stimulating lipid accumulation, foam cell formation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages. Adipokines can also promote balance or resolution during metabolic and immune processes by promoting reverse lipid transport and expression of Th2 cytokines. This review will explore the mechanisms by which catecholamines and adipokines influence macrophage function in neural pathways, immunity and metabolism.
Keywords: Adipokine; Atherosclerosis; Dopamine; Macrophage; Resistin-like molecules.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The crosstalks between adipokines and catecholamines.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011 Jan 30;332(1-2):261-70. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.11.002. Epub 2010 Nov 9. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21070834
-
[Adipokines: adiponectin, leptin, resistin and coronary heart disease risk].Przegl Lek. 2005;62 Suppl 3:69-72. Przegl Lek. 2005. PMID: 16521924 Review. Polish.
-
Signalling mechanisms underlying the metabolic and other effects of adipokines on the heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Jul 15;79(2):279-86. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn115. Epub 2008 May 12. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18474523 Review.
-
Inflammatory markers and adipokines alter adipocyte-derived ASP production through direct and indirect immune interaction.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2013 Apr;121(4):194-200. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1333231. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23430572
-
Innate immunity modulates adipokines in humans.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Jun;92(6):2272-9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-2545. Epub 2007 Mar 20. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17374708 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Diet-Induced Obesity Elicits Macrophage Infiltration and Reduction in Spine Density in the Hypothalami of Male but Not Female Mice.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 11;9:1992. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01992. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30254630 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Macrophage Dopamine Receptors in Mediating Cytokine Production: Implications for Neuroinflammation in the Context of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019 Mar;14(1):134-156. doi: 10.1007/s11481-018-9825-2. Epub 2018 Dec 5. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30519866 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Studies on the Role of Neuroendocrine Disorders in Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome-Related Atherosclerosis.Nat Sci Sleep. 2021 Jul 27;13:1331-1345. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S315375. eCollection 2021. Nat Sci Sleep. 2021. PMID: 34349578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory actions of (-)-epicatechin in the adipose tissue of obese mice.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Dec;81(Pt B):383-392. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.08.044. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27592457 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-based Scores in Patients With Pheochromocytoma.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Feb 18;110(3):e630-e640. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae284. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 38655872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Musso NR, Brenci S, Setti M, Indiveri F, Lotti G. Catecholamine content and in vitro catecholamine synthesis in peripheral human lymphocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:3553–7. - PubMed
-
- Watkins LR, Goehler LE, Relton JK, Tartaglia N, Silbert L, Martin D, et al. Blockade of interleukin-1 induced hyperthermia by subdiaphragmatic vagotomy: evidence for vagal mediation of immune-brain communication. Neurosci Lett. 1995;183:27–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

