Normal values of Hertel exophthalmometry in a Chinese Han population from Shenyang, Northeast China
- PMID: 25703959
- PMCID: PMC4336939
- DOI: 10.1038/srep08526
Normal values of Hertel exophthalmometry in a Chinese Han population from Shenyang, Northeast China
Abstract
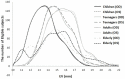
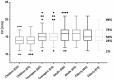
Aims of this study were to determine the normal range of absolute and relative Hertel exophthalmometric values (EVs) in a Chinese Han population. This population-based cross-sectional study consisted of 2010 healthy Han Chinese (1051 females and 959 males) aged between 8-87 years living in Shenyang, Northeast China, including 515 children (aged 8-14 years), 517 teenagers (aged 15-19 years), 582 adults (aged 20-69 years) and 396 elderly (aged 70-87 years). A Hertel exophthalmometer was used by the same physician for the measurement of EV and inter-orbital distance (IOD). For the entire study population, the Hertel EVs ranged from 10 mm to 22 mm; the mean EVs for the left eye (OS) and right eye (OD) were 15.0 ± 1.9 mm and 15.0 ± 2.0 mm, respectively; the upper normal limits of the EVs (mean + 2 SD) for OS and OD were 18.8 mm and 19.0 mm, respectively; the mean relative EV was 0.20 ± 0.43 mm. Age, but not sex, had a significant effect on the EV. We concluded that our study provides normative ophthalmic data in a Chinese Han population. The normal EVs, asymmetry and IOD values have been established for clinical reference.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Normal values of hertel exophthalmometry in children, teenagers, and adults from Tehran, Iran.Optom Vis Sci. 2008 Oct;85(10):1012-7. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0b013e3181890dc7. Optom Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18832980
-
Normative exophthalmometry values in Hispanic individuals.Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol (Engl Ed). 2023 Apr;98(4):199-205. doi: 10.1016/j.oftale.2023.02.002. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol (Engl Ed). 2023. PMID: 36738924
-
Reliability of exophthalmos measurement and the exophthalmometry value distribution in a healthy Dutch population and in Graves' patients. An exploratory study.Orbit. 2004 Sep;23(3):161-8. doi: 10.1080/01676830490504089. Orbit. 2004. PMID: 15545129
-
Normal values of ocular protrusion in Saudi Arabian male children.Optom Vis Sci. 1995 Aug;72(8):557-64. doi: 10.1097/00006324-199508000-00004. Optom Vis Sci. 1995. PMID: 8539023 Review.
-
Parallax-free exophthalmometry: a comprehensive review of the literature on clinical exophthalmometry and the introduction of the first parallax-free exophthalmometer.Orbit. 2015 Feb;34(1):23-9. doi: 10.3109/01676830.2014.963877. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Orbit. 2015. PMID: 25313439 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical characteristics of moderate-to-severe thyroid associated ophthalmopathy in 354 Chinese cases.PLoS One. 2017 May 4;12(5):e0176064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176064. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28472149 Free PMC article.
-
Hertel Exophthalmometry Values in a Greek Adult Outpatient Clinic-Based Population: Association With Demographic Factors and Systemic Disease.Cureus. 2023 Feb 15;15(2):e35027. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35027. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36938254 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of rituximab in treating steroid-resistant Graves' orbitopathy in active moderate-to-severe and sight-threatening forms: A retrospective observation from China.Heliyon. 2024 May 28;10(11):e31932. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31932. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38867959 Free PMC article.
-
Normal Exophthalmometry Values in Iranian Population: A Meta-analysis.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2021 Jul 29;16(3):470-477. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v16i3.9441. eCollection 2021 Jul-Sep. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2021. PMID: 34394874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current insights of applying MRI in Graves' ophthalmopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 29;13:991588. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.991588. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36267571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grove A. S. Evaluation of exophthalmos. N. Engl. J. Med 292, 1005–1013 (1975). - PubMed
-
- Smolders M. H. et al. Exophthalmos in obesity. Ophthalmic. Res 36, 78–81 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Chan W. et al. Exophthalmometric values and their biometric correlates: The Kandy Eye Study. Clin. Experiment. Ophthalmol 37, 496–502 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Onofrey B. E., Skorin L. Jr & Holdeman N. R. Ocular therapeutics handbook: a clinical manual (Third Edition).[Onofrey B. E., (ed.)] [71–72](Wolters Kluwer, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2011.)
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources