Role of the Sigma-1 receptor in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- PMID: 25704013
- PMCID: PMC4489701
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jphs.2014.12.013
Role of the Sigma-1 receptor in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Abstract
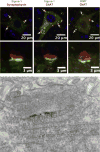
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting spinal cord motoneurons (MN) with an associative connection to Frontotemporal Lobar Dementia (FTLD). The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) bound Sigma-1 Receptor (S1R) chaperone protein localizes to specialized ER cisternae within 10 nm of the plasma membrane in spinal cord ventral horn cholinergic post synaptic C-terminals. Removal of the S1R gene in the Superoxide Dismutase-1 (SOD-1) mouse model of ALS exacerbated the neurodegenerative condition and resulted in a significantly reduced longevity when compared to the SOD-1/S1R wild type (WT) mouse. The proposed amelioration of the ALS phenotype by the S1R is likely due to a "brake" on excitation of the MN as evidenced by a reduction in action potential generation in the MN of the WT when compared to the S1R KO mouse MN. Although the precise signal transduction pathway(s) regulated by the S1R in the MN has/have not been elucidated at present, it is likely that direct or indirect functional interactions occur between the S1R in the ER cisternae with voltage gated potassium channels and/or with muscarinic M2 receptor signaling in the post synaptic plasma membrane. Possible mechanisms for regulation of MN excitability by S1R are discussed.
Keywords: ALS; C-terminals; Motoneurons; Sigma-1 receptor.
Copyright © 2015 Japanese Pharmacological Society. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

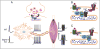
References
-
- Boillee S, Vande Velde C, Cleveland DW. ALS: a disease of motor neurons and their nonneuronal neighbors. Neuron. 2006;52:39–59. - PubMed
-
- Abel O, Powell JF, Andersen PM, Al-Chalabi A. ALSoD: a user-friendly online bioinformatics tool for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis genetics. Hum Mutat. 2012;33:1345–1351. - PubMed
-
- Al-Saif A, Al-Mohanna F, Bohlega S. A mutation in sigma-1 receptor causes juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2011;70:913–919. - PubMed
-
- Marin B, Kacem I, Diagana M, Boulesteix M, Gouider R, Preux PM, et al. Juvenile and adult-onset ALS/MND among Africans: incidence, phenotype, survival: a review. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2012;13:276–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

