CDK6 levels regulate quiescence exit in human hematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 25704240
- PMCID: PMC4359055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.01.017
CDK6 levels regulate quiescence exit in human hematopoietic stem cells
Abstract
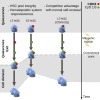
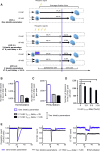
Regulated blood production is achieved through the hierarchical organization of dormant hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) subsets that differ in self-renewal potential and division frequency, with long-term (LT)-HSCs dividing the least. The molecular mechanisms underlying this variability in HSC division kinetics are unknown. We report here that quiescence exit kinetics are differentially regulated within human HSC subsets through the expression level of CDK6. LT-HSCs lack CDK6 protein. Short-term (ST)-HSCs are also quiescent but contain high CDK6 protein levels that permit rapid cell cycle entry upon mitogenic stimulation. Enforced CDK6 expression in LT-HSCs shortens quiescence exit and confers competitive advantage without impacting function. Computational modeling suggests that this independent control of quiescence exit kinetics inherently limits LT-HSC divisions and preserves the HSC pool to ensure lifelong hematopoiesis. Thus, differential expression of CDK6 underlies heterogeneity in stem cell quiescence states that functionally regulates this highly regenerative system.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Benveniste P., Frelin C., Janmohamed S., Barbara M., Herrington R., Hyam D., Iscove N.N. Intermediate-term hematopoietic stem cells with extended but time-limited reconstitution potential. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;6:48–58. - PubMed
-
- Bradford G.B., Williams B., Rossi R., Bertoncello I. Quiescence, cycling, and turnover in the primitive hematopoietic stem cell compartment. Exp. Hematol. 1997;25:445–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

