Dysregulated CXCR4 expression promotes lymphoma cell survival and independently predicts disease progression in germinal center B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 25704881
- PMCID: PMC4467389
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3343
Dysregulated CXCR4 expression promotes lymphoma cell survival and independently predicts disease progression in germinal center B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
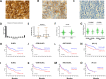
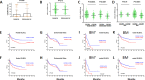
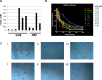
Abnormal expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 plays an essential role in tumor cell dissemination and disease progression. However, the significance of CXCR4 overexpression in de novo diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is unknown. In 743 patients with de novo diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who received standard Rituximab-CHOP immunochemotherapy, we assessed the expression of CXCR4 and dissected its prognostic significance in various DLBCL subsets. Our results showed that CXCR4+ patients was associated with male, bulky tumor, high Ki-67 index, activated B-cell-like (ABC) subtype, and Myc, Bcl-2 or p53 overexpression. Moreover, CXCR4+ was an independent factor predicting poorer progression-free survival in germinal-center B-cell-like (GCB)-DLBCL, but not in ABC-DLBCL; and in patients with an IPI of ≤2, but not in those with an IPI>2. The lack of prognostic significance of CXCR4 in ABC-DLBCL was likely due to the activation of p53 tumor suppressor attenuating CXCR4 signaling. Furthermore, concurrent CXCR4+ and BCL2 translocation showed dismal outcomes resembling but independent of MYC/BCL2 double-hit DLBCL. Gene expression profiling suggested that alterations in the tumor microenvironment and immune responses, increased tumor proliferation and survival, and the dissemination of CXCR4+ tumor cells to distant organs or tissues were underlying molecular mechanisms responsible for the CXCR4+ associated poor prognosis.
Keywords: BCL2; CXCR4; DLBCL; Myc; TP53 mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical Impact of the Cell-of-Origin Classification and the MYC/ BCL2 Dual Expresser Status in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated Within Prospective Clinical Trials of the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Study Group.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Aug 1;35(22):2515-2526. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.70.3660. Epub 2017 May 19. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28525305 Clinical Trial.
-
Assessment of CD37 B-cell antigen and cell of origin significantly improves risk prediction in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Blood. 2016 Dec 29;128(26):3083-3100. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-05-715094. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27760757 Free PMC article.
-
Double-Hit Gene Expression Signature Defines a Distinct Subgroup of Germinal Center B-Cell-Like Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan 20;37(3):190-201. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01583. Epub 2018 Dec 3. J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30523716 Free PMC article.
-
The Spectrum of MYC Alterations in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Acta Haematol. 2020;143(6):520-528. doi: 10.1159/000505892. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Acta Haematol. 2020. PMID: 32074595 Review.
-
Should We Use Cell of Origin and Dual-protein Expression in Treating DLBCL?Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Feb;18(2):91-97. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.12.003. Epub 2017 Dec 24. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018. PMID: 29352717 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic efficacy of the RTN1 gene in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 26;11(1):21098. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00746-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34702929 Free PMC article.
-
18F-FDG PET Dissemination Features in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Are Predictive of Outcome.J Nucl Med. 2020 Jan;61(1):40-45. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.119.229450. Epub 2019 Jun 14. J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 31201248 Free PMC article.
-
Selective delivery of T22-PE24-H6 to CXCR4+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells leads to wide therapeutic index in a disseminated mouse model.Theranostics. 2020 Apr 6;10(12):5169-5180. doi: 10.7150/thno.43231. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32373205 Free PMC article.
-
Response assessment with the CXCR4-directed positron emission tomography tracer [68Ga]Pentixafor in a patient with extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of the orbital cavities.EJNMMI Res. 2017 Dec;7(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13550-017-0294-z. Epub 2017 Jun 2. EJNMMI Res. 2017. PMID: 28577295 Free PMC article.
-
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: R-CHOP failure-what to do?Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2016 Dec 2;2016(1):366-378. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2016.1.366. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2016. PMID: 27913503 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mehta SA, Christopherson KW, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Goulet RJ, Jr, Broxmeyer HE, Kopelovich L, Nakshatri H. Negative regulation of chemokine receptor CXCR4 by tumor suppressor p53 in breast cancer cells: implications of p53 mutation or isoform expression on breast cancer cell invasion. Oncogene. 2007;26:3329–37. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida N, Kitayama D, Arima M, Sakamoto A, Inamine A, Watanabe-Takano H, Hatano M, Koike T, Tokuhisa T. CXCR4 expression on activated B cells is downregulated by CD63 and IL-21. J Immunol. 2011;186:2800–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

