Factors influencing adverse skin responses in rats receiving repeated subcutaneous injections and potential impact on neurobehavior
- PMID: 25705100
- PMCID: PMC4334164
Factors influencing adverse skin responses in rats receiving repeated subcutaneous injections and potential impact on neurobehavior
Abstract
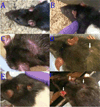
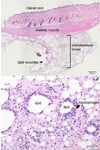
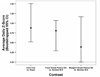
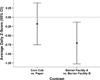
Repeated subcutaneous (s.c.) injection is a common route of administration in chronic studies of neuroactive compounds. However, in a pilot study we noted a significant incidence of skin abnormalities in adult male Long-Evans rats receiving daily s.c. injections of peanut oil (1.0 ml/kg) in the subscapular region for 21 d. Histopathological analyses of the lesions were consistent with a foreign body reaction. Subsequent studies were conducted to determine factors that influenced the incidence or severity of skin abnormalities, and whether these adverse skin reactions influenced a specific neurobehavioral outcome. Rats injected daily for 21 d with food grade peanut oil had an earlier onset and greater incidence of skin abnormalities relative to rats receiving an equal volume (1.0 ml/kg/d) of reagent grade peanut oil or triglyceride of coconut oil. Skin abnormalities in animals injected daily with peanut oil were increased in animals housed on corncob versus paper bedding. Comparison of animals obtained from different barrier facilities exposed to the same injection paradigm (reagent grade peanut oil, 1.0 ml/kg/d s.c.) revealed significant differences in the severity of skin abnormalities. However, animals from different barrier facilities did not perform differently in a Pavlovian fear conditioning task. Collectively, these data suggest that environmental factors influence the incidence and severity of skin abnormalities following repeated s.c. injections, but that these adverse skin responses do not significantly influence performance in at least one test of learning and memory.
Keywords: adverse skin reaction; foreign body reaction; learning and memory; neurobehavior; peanut oil; subcutaneous injection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Theophylline (CAS No. 58-55-9) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Feed and Gavage Studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1998 Aug;473:1-326. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1998. PMID: 12571677
-
Final report on the safety assessment of capsicum annuum extract, capsicum annuum fruit extract, capsicum annuum resin, capsicum annuum fruit powder, capsicum frutescens fruit, capsicum frutescens fruit extract, capsicum frutescens resin, and capsaicin.Int J Toxicol. 2007;26 Suppl 1:3-106. doi: 10.1080/10915810601163939. Int J Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17365137 Review.
-
Final report on the safety assessment of Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) Oil, Hydrogenated Peanut Oil, Peanut Acid, Peanut Glycerides, and Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) Flour.Int J Toxicol. 2001;20 Suppl 2:65-77. doi: 10.1080/10915810160233776. Int J Toxicol. 2001. PMID: 11558642 Review.
-
NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Coumarin (CAS No. 91-64-5) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Gavage Studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1993 Sep;422:1-340. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1993. PMID: 12616289
-
NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of o-Benzyl-p-Chlorophenol (CAS No. 120-32-1) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Gavage Studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1994 Jan;424:1-304. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1994. PMID: 12616287
Cited by
-
Acute or Chronic Exposure to Corticosterone Promotes Wakefulness in Mice.Brain Sci. 2023 Oct 18;13(10):1472. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13101472. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37891839 Free PMC article.
-
Facile design of lidocaine-loaded polymeric hydrogel to persuade effects of local anesthesia drug delivery system: complete in vitro and in vivo toxicity analyses.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):1080-1092. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1931558. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34114924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Final report on the safety assessment of Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) Oil, Hydrogenated Peanut Oil, Peanut Acid, Peanut Glycerides, and Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) Flour. Int J Toxicol. 2001;20(Suppl)(2):65–77. - PubMed
-
- Ader R, Felten D, Cohen N. Interactions between the brain and the immune system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:561–602. - PubMed
-
- Pugh CR, Nguyen KT, Gonyea JL, Fleshner M, Wakins LR, Maier SF, Rudy JW. Role of interleukin-1 beta in impairment of contextual fear conditioning caused by social isolation. Behav Brain Res. 1999;106:109–118. - PubMed
-
- Coleman DL, King RN, Andrade JD. The foreign body reaction: a chronic inflammatory response. J Biomed Mater Res. 1974;8:199–211. - PubMed
