Greater general startle reflex is associated with greater anxiety levels: a correlational study on 111 young women
- PMID: 25705181
- PMCID: PMC4319476
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00010
Greater general startle reflex is associated with greater anxiety levels: a correlational study on 111 young women
Abstract
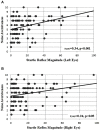
Startle eyeblink reflex is a valid non-invasive tool for studying attention, emotion and psychiatric disorders. In the absence of any experimental manipulation, the general (or baseline) startle reflex shows a high inter-individual variability, which is often considered task-irrelevant and therefore normalized across participants. Unlike the above view, we hypothesized that greater general startle magnitude is related to participants' higher anxiety level. 111 healthy young women, after completing the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI), were randomly administered 10 acoustic white noise probes (50 ms, 100 dBA acoustic level) while integrated EMG from left and right orbicularis oculi was recorded. Results showed that participants with greater state anxiety levels exhibited larger startle reflex magnitude from the left eye (r 109 = 0.23, p < 0.05). Furthermore, individuals who perceived the acoustic probe as more aversive reported the largest anxiety scores (r 109 = 0.28, p < 0.05) and had the largest eyeblinks, especially in the left eye (r 109 = 0.34, p < 0.001). Results suggest that general startle may represent a valid tool for studying the neural excitability underlying anxiety and emotional dysfunction in neurological and mental disorders.
Keywords: EMG; anxiety; baseline startle reflex; emotion; laterality; noise aversiveness.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fear-potentiated startle: relationship to the level of state/trait anxiety in healthy subjects.Biol Psychiatry. 1993 Apr 15-May 1;33(8-9):566-74. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(93)90094-t. Biol Psychiatry. 1993. PMID: 8329489
-
Does trait anxiety influence effects of oxytocin on eye-blink startle reactivity? A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 4;13(1):e0190809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190809. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29300752 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of personality trait emotionality on acoustic startle response and prepulse inhibition including N100 and P200 event-related potential.Clin Neurophysiol. 2013 Feb;124(2):292-305. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2012.07.018. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Clin Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 22938794
-
The fear potentiated startle effect. Blink reflex modulation as a result of classical aversive conditioning.Integr Physiol Behav Sci. 1991 Apr-Jun;26(2):119-26. doi: 10.1007/BF02691034. Integr Physiol Behav Sci. 1991. PMID: 1878318 Clinical Trial.
-
Startle reflex modification: emotion or attention?Psychophysiology. 1990 Sep;27(5):513-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1990.tb01966.x. Psychophysiology. 1990. PMID: 2274614
Cited by
-
The Impact of Chronic Phthalate Exposure on Rodent Anxiety and Cognition.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2023 Jul 21;4(1):203-212. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2023.07.002. eCollection 2024 Jan. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2023. PMID: 38298799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen receptor beta in the central amygdala regulates the deleterious behavioral and neuronal consequences of repeated social stress in female rats.Neurobiol Stress. 2023 Feb 21;23:100531. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2023.100531. eCollection 2023 Mar. Neurobiol Stress. 2023. PMID: 36879670 Free PMC article.
-
How representative are neuroimaging samples? Large-scale evidence for trait anxiety differences between fMRI and behaviour-only research participants.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2021 Sep 30;16(10):1057-1070. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsab057. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33950220 Free PMC article.
-
Welfare-improving enrichments greatly reduce hens' startle responses, despite little change in judgment bias.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 15;9(1):11881. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48351-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31417122 Free PMC article.
-
The relation of neuroticism to physiological and behavioral stress responses induced by auditory startle.Brain Behav. 2022 May;12(5):e2554. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2554. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Brain Behav. 2022. PMID: 35403836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angrilli A. (1995). PSAAL: a LabVIEW 3 program for data acquisition and analysis in psychophysiological experiments. Behav. Res. Meth. Instr. Computers 27, 367–374 10.3758/bf03200431 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

