PAMPs and DAMPs as triggers for DIC
- PMID: 25705424
- PMCID: PMC4336279
- DOI: 10.1186/s40560-014-0065-0
PAMPs and DAMPs as triggers for DIC
Abstract
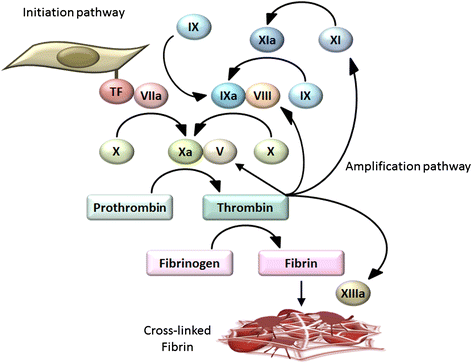
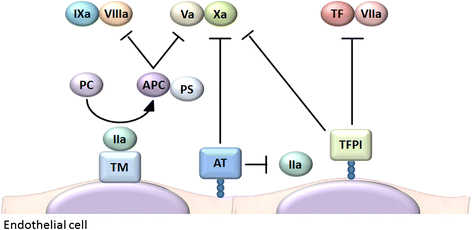
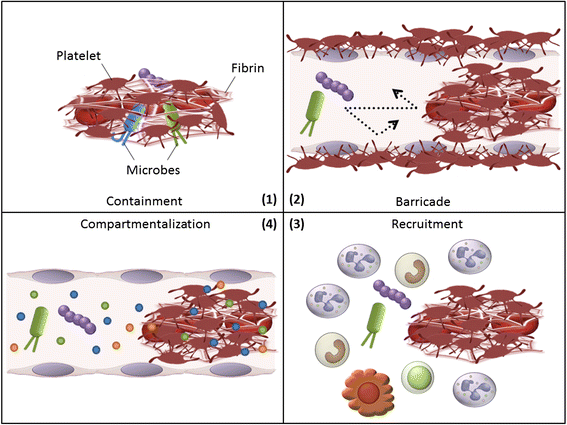
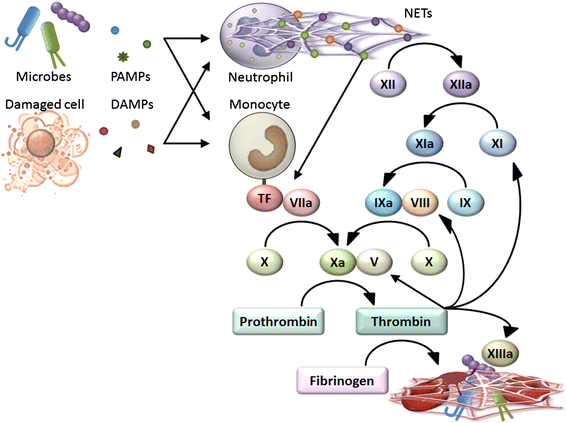
Thrombosis is generally considered harmful because it compromises the blood supply to organs. However, recent studies have suggested that thrombosis under certain circumstances plays a major physiological role in early immune defense against invading pathogens. This defensive role of thrombosis is now referred to as immunothrombosis. Activated monocytes and neutrophils are two major inducers of immunothrombosis. Monocytes and neutrophils are activated when they detect pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). Detection of PAMPs and DAMPs triggers tissue factor expression on monocytes and neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) release by neutrophils, promoting immunothrombosis. Although tissue factor-mediated and NET-mediated immunothrombosis plays a role in early host defense against bacterial dissemination, uncontrolled immunothrombosis may lead to disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Keywords: Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs); Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC); Immunothrombosis; Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs); Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs); Tissue factor.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

