Organizing Pneumonia Associated with Pegylated Interferon α and Ribavirin Therapy
- PMID: 25705538
- PMCID: PMC4325218
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/794592
Organizing Pneumonia Associated with Pegylated Interferon α and Ribavirin Therapy
Abstract
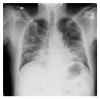
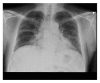
Hepatitis C virus infection is the leading cause of chronic liver disease in the United States of America. Pegylated interferon α and ribavirin combination is the mainstay of treatment. Severe pulmonary toxicities are rarely reported. We report here a case of severe form of organizing pneumonia secondary to pegylated interferon α therapy presenting as acute respiratory failure. Patient has near complete recovery with withdrawal of pegylated interferon α and steroid therapy. We report this case to raise the awareness of this rare but potentially life-threatening pulmonary complication of pegylated interferon α therapy.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

