Potts shunt in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 25705598
- PMCID: PMC4333855
- DOI: 10.5090/kjtcs.2015.48.1.52
Potts shunt in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
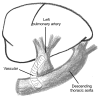
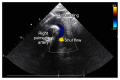
Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension eventually leads to right-sided heart failure and sudden death. Its mortality rate in children is still high, despite improvements in pharmacological therapy, and therefore novel treatments are necessary. The Potts shunt, which creates an anastomosis between the left pulmonary artery and the descending aorta, has been proposed as a theoretically promising palliative surgical technique to decompress the right ventricle. We report the case of a 12-year-old girl with suprasystemic idiopathic pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular failure who underwent a Potts shunt for palliation with good short-term results.
Keywords: Pulmonary hypertension; Shunts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surgical palliation of primary pulmonary arterial hypertension by a unidirectional valved Potts anastomosis in an animal model.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011 Nov;142(5):1223-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.10.060. Epub 2011 May 17. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011. PMID: 21592527
-
Potts shunt in children with pulmonary arterial hypertension: institutional experience.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2017 Oct 1;25(4):595-599. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivx209. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2017. PMID: 28679172
-
Anesthetic management of children with medically refractory pulmonary hypertension undergoing surgical Potts shunt.Paediatr Anaesth. 2024 Jan;34(1):79-85. doi: 10.1111/pan.14764. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Paediatr Anaesth. 2024. PMID: 37800662
-
Anesthetic management for percutaneous reverse Potts shunt creation in children with refractory idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: A case series.Paediatr Anaesth. 2021 Jun;31(6):644-649. doi: 10.1111/pan.14169. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Paediatr Anaesth. 2021. PMID: 33683767 Review.
-
Reversed Potts Shunt Outcome in Suprasystemic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2022;18(6):e090522204486. doi: 10.2174/1573403X18666220509203335. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35538823 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing With Forehead and Popliteal Oximetry in Evaluating Efficacy of Reverse Potts Shunt.JACC Case Rep. 2025 Apr 2;30(7):103409. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2025.103409. JACC Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40185583 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Therapies for Right Ventricular Failure.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025 Jan 18;27(1):26. doi: 10.1007/s11886-024-02157-9. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39825962 Review.
-
Assessment and treatment of the failing right heart: considerations for transplantation referral.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Sep;11(Suppl 14):S1817-S1820. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.08.60. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31632759 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thoele DG, Barst RJ, Gersony WM. Physiologic-based management of primary pulmonary hypertension in children and young adults. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990;15:242A. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(90)92680-Z. - DOI
-
- Hopkins WE, Ochoa LL, Richardson GW, Trulock EP. Comparison of the hemodynamics and survival of adults with severe primary pulmonary hypertension or Eisenmenger syndrome. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1996;15(1 Pt 1):100–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources