Osteonecrosis of the knee: review
- PMID: 25705638
- PMCID: PMC4293480
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2014.11.13
Osteonecrosis of the knee: review
Abstract
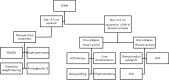
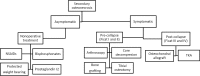
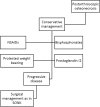
Osteonecrosis is a devastating disease that can lead to end-stage arthritis of various joint including the knee. There are three categories of osteonecrosis that affect the knee: spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee (SONK), secondary, and post-arthroscopic. Regardless of osteonecrosis categories, the treatment of this disease aims to halt further progression or delay the onset of end-stage arthritis of the knee. However, once substantial joint surface collapse has occurred or there are sign of degenerative arthritis, joint arthroplasty is the most appropriate treatment option. Currently, the non-operative treatment options consist of observation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), protected weight bearing, and analgesia as needed. Operative interventions include joint preserving surgery, unilateral knee arthroplasty (UKA), or total knee arthroplasty (TKA) depending on the extent and type of disease. Joint preserving procedures (i.e., arthroscopy, core decompression, osteochondral autograft, and bone grafting) are usually attempted in pre-collapse and some post-collapse lesions, when the articular cartilage is generally intact with only the underlying subchondral bone being affected. Conversely, after severe subchondral collapse has occurred, procedures that attempt to salvage the joint are rarely successful and joint arthroplasty are necessary to relieve pain. The purpose of this article is to highlight the recent evidence concerning the treatment options across the spectrum of management of osteonecrosis of the knee including lesion observation, medications, joint preserving techniques, and total joint arthroplasties.
Keywords: Avascular necrosis; arthroplasty; knee pain; osteonecrosis; postarthroscopic osteonecrosis; spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee (SONK).
Figures
References
-
- Ahlbäck S, Bauer GC, Bohne WH. Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum 1968;11:705-33. - PubMed
-
- Mont MA, Baumgarten KM, Rifai A, et al. Atraumatic osteonecrosis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2000;82:1279-90. - PubMed
-
- Pape D, Seil R, Fritsch E, et al. Prevalence of spontaneous osteonecrosis of the medial femoral condyle in elderly patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2002;10:233-40. - PubMed
-
- Cetik O, Cift H, Comert B, et al. Risk of osteonecrosis of the femoral condyle after arthroscopic chondroplasty using radiofrequency: a prospective clinical series. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2009;17:24-9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
