Early hyperlipidemia promotes endothelial activation via a caspase-1-sirtuin 1 pathway
- PMID: 25705917
- PMCID: PMC4376583
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305282
Early hyperlipidemia promotes endothelial activation via a caspase-1-sirtuin 1 pathway
Abstract
Objective: The role of receptors for endogenous metabolic danger signals-associated molecular patterns has been characterized recently as bridging innate immune sensory systems for danger signals-associated molecular patterns to initiation of inflammation in bone marrow-derived cells, such as macrophages. However, it remains unknown whether endothelial cells (ECs), the cell type with the largest numbers and the first vessel cell type exposed to circulating danger signals-associated molecular patterns in the blood, can sense hyperlipidemia. This report determined whether caspase-1 plays a role in ECs in sensing hyperlipidemia and promoting EC activation.
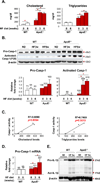
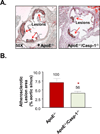
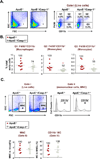
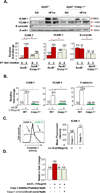
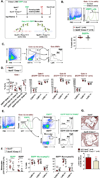
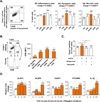
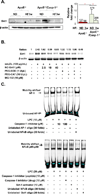
Approach and results: Using biochemical, immunologic, pathological, and bone marrow transplantation methods together with the generation of new apoplipoprotein E (ApoE)(-/-)/caspase-1(-/-) double knockout mice, we made the following observations: (1) early hyperlipidemia induced caspase-1 activation in ApoE(-/-) mouse aorta; (2) caspase-1(-/-)/ApoE(-/-) mice attenuated early atherosclerosis; (3) caspase-1(-/-)/ApoE(-/-) mice had decreased aortic expression of proinflammatory cytokines and attenuated aortic monocyte recruitment; and (4) caspase-1(-/-)/ApoE(-/-) mice had decreased EC activation, including reduced adhesion molecule expression and cytokine secretion. Mechanistically, oxidized lipids activated caspase-1 and promoted pyroptosis in ECs by a reactive oxygen species mechanism. Caspase-1 inhibition resulted in accumulation of sirtuin 1 in the ApoE(-/-) aorta, and sirtuin 1 inhibited caspase-1 upregulated genes via activator protein-1 pathway.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate for the first time that early hyperlipidemia promotes EC activation before monocyte recruitment via a caspase-1-sirtuin 1-activator protein-1 pathway, which provides an important insight into the development of novel therapeutics for blocking caspase-1 activation as early intervention of metabolic cardiovascular diseases and inflammations.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; caspase-1; inflammation.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early inflammatory reactions in atherosclerosis are induced by proline-rich tyrosine kinase/reactive oxygen species-mediated release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and subsequent activation of the p21Cip1/Ets-1/p300 system.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 May;31(5):1084-92. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.221804. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. Retraction in: Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Apr;34(4):e6. doi: 10.1161/ATV.0000000000000005. PMID: 21372295 Retracted.
-
Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Mediate Lysophosphatidylcholine-Induced Endothelial Cell Activation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Jun;36(6):1090-100. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306964. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27127201 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Hic-5 in the formation of microvilli-like structures and the monocyte-endothelial interaction that accelerates atherosclerosis.Cardiovasc Res. 2015 Mar 1;105(3):361-71. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv003. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Cardiovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 25587044
-
SIRT1 - an anti-inflammatory pathway at the crossroads between metabolic disease and atherosclerosis.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2012 Nov;10(6):693-6. doi: 10.2174/157016112803520756. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23259556 Review.
-
Mouse models of hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis.Front Biosci. 2001 Mar 1;6:D515-25. doi: 10.2741/fazio. Front Biosci. 2001. PMID: 11229870 Review.
Cited by
-
The emerging role of pyroptosis-related inflammasome pathway in atherosclerosis.Mol Med. 2022 Dec 21;28(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00594-2. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36544112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aorta in Pathologies May Function as an Immune Organ by Upregulating Secretomes for Immune and Vascular Cell Activation, Differentiation and Trans-Differentiation-Early Secretomes may Serve as Drivers for Trained Immunity.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 7;13:858256. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.858256. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35320939 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Endothelial Cells and Innate Immunity.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Jun;40(6):e138-e152. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314330. Epub 2020 May 27. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32459541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysophospholipid Receptors, as Novel Conditional Danger Receptors and Homeostatic Receptors Modulate Inflammation-Novel Paradigm and Therapeutic Potential.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2016 Aug;9(4):343-59. doi: 10.1007/s12265-016-9700-6. Epub 2016 May 26. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27230673 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Immunity on Coronary Artery Disease: An Updated Pathogenic Interplay and Potential Therapeutic Strategies.Life (Basel). 2023 Oct 27;13(11):2128. doi: 10.3390/life13112128. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004268 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2011;473:317–325. - PubMed
-
- Zhang D, Jiang X, Fang P, Yan Y, Song J, Gupta S, Schafer AI, Durante W, Kruger WD, Yang X, Wang H. Hyperhomocysteinemia promotes inflammatory monocyte generation and accelerates atherosclerosis in transgenic cystathionine beta-synthase-deficient mice. Circulation. 2009;120:1893–1902. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Combadiere C, Potteaux S, Rodero M, Simon T, Pezard A, Esposito B, Merval R, Proudfoot A, Tedgui A, Mallat Z. Combined inhibition of ccl2, cx3cr1, and ccr5 abrogates ly6c(hi) and ly6c(lo) monocytosis and almost abolishes atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic mice. Circulation. 2008;117:1649–1657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

