Exercise Augmentation of Exposure Therapy for PTSD: Rationale and Pilot Efficacy Data
- PMID: 25706090
- PMCID: PMC4464974
- DOI: 10.1080/16506073.2015.1012740
Exercise Augmentation of Exposure Therapy for PTSD: Rationale and Pilot Efficacy Data
Abstract
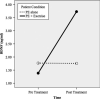
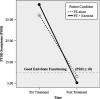
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is associated with synaptic plasticity, which is crucial for long-term learning and memory. Some studies suggest that people suffering from anxiety disorders show reduced BDNF relative to healthy controls. Lower BDNF is associated with impaired learning, cognitive deficits, and poor exposure-based treatment outcomes. A series of studies with rats showed that exercise elevates BDNF and enhances fear extinction. However, this strategy has not been tested in humans. In this pilot study, we randomized participants (N = 9, 8 females, M(Age) = 34) with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) to (a) prolonged exposure alone (PE) or (b) prolonged exposure+exercise (PE+E). Participants randomized to the PE+E condition completed a 30-minute bout of moderate-intensity treadmill exercise (70% of age-predicted HR(max)) prior to each PE session. Consistent with prediction, the PE+E group showed a greater improvement in PTSD symptoms (d = 2.65) and elevated BDNF (d = 1.08) relative to the PE only condition. This pilot study provides initial support for further investigation into exercise augmented exposure therapy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01199107.
Keywords: BDNF; CBT; anxiety disorders; augmentation; exercise; exposure therapy; pilot data.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A pilot study of the role of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in response to exercise-augmented exposure therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2024 Sep;167:107106. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2024.107106. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38943720
-
Augmenting Prolonged Exposure therapy for PTSD with intranasal oxytocin: A randomized, placebo-controlled pilot trial.J Psychiatr Res. 2018 Mar;98:64-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2017.12.014. Epub 2017 Dec 26. J Psychiatr Res. 2018. PMID: 29294429 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cortisol augmentation of a psychological treatment for warfighters with posttraumatic stress disorder: Randomized trial showing improved treatment retention and outcome.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015 Jan;51:589-97. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.08.004. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25212409 Clinical Trial.
-
Exposure-based therapy for post-traumatic stress disorder in children and adults.Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci. 2009;46(4):274-81. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci. 2009. PMID: 20635775 Review.
-
[Treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder and extinction learning of traumatic memory].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2013 Jun;33(3):111-5. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2013. PMID: 25069244 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Exercise for Mood and Anxiety Disorders: The State-of-the Science.Cogn Behav Ther. 2015;44(4):237-9. doi: 10.1080/16506073.2015.1047286. Cogn Behav Ther. 2015. PMID: 26057087 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Post-traumatic stress disorder: a state-of-the-art review of evidence and challenges.World Psychiatry. 2019 Oct;18(3):259-269. doi: 10.1002/wps.20656. World Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31496089 Free PMC article.
-
Augmenting PTSD treatment with physical activity: study protocol of the APPART study (Augmentation for PTSD with Physical Activity in a Randomized Trial).Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2022 Jan 31;13(1):2016219. doi: 10.1080/20008198.2021.2016219. eCollection 2022. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2022. PMID: 35126881 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Acute exercise enhances the consolidation of fear extinction memory and reduces conditioned fear relapse in a sex-dependent manner.Learn Mem. 2017 Jul 17;24(8):358-368. doi: 10.1101/lm.045195.117. Print 2017 Aug. Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28716955 Free PMC article.
-
Posttraumatic stress disorder increases thrombosis risk: Evidence from a biobank data set.Am J Hematol. 2024 Dec;99(12):2279-2285. doi: 10.1002/ajh.27468. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Am J Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39207181
References
-
- Akers KG, Martinez-Canabal A, Restivo L, Yiu AP, Cristofaro AD, Hsiang H.-L.(Liz), Frankland PW. Hippocampal neurogenesis regulates forgetting during adulthood and infancy. Science. 2014;344:598–602. doi:10.1126/science.1248903. - PubMed
-
- American College for Sports Medicine . ACSM's guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2013.
-
- Angelucci F, Gelfo F, De Bartolo P, Caltagirone C, Petrosini L. BDNF concentrations are decreased in serum and parietal cortex in immunotoxin 192 IgG-Saporin rat model of cholinergic degeneration. Neurochemistry International. 2011;59(1):1–4. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2011.04.010. - PubMed
-
- Arancio O, Chao MV. Neurotrophins, synaptic plasticity and dementia. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 2007;17:325–330. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2007.03.013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical