Neuronal ensembles sufficient for recovery sleep and the sedative actions of α2 adrenergic agonists
- PMID: 25706476
- PMCID: PMC4836567
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3957
Neuronal ensembles sufficient for recovery sleep and the sedative actions of α2 adrenergic agonists
Abstract
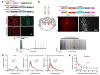
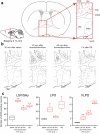
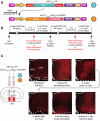
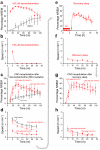
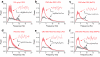
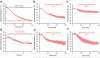
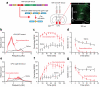
Do sedatives engage natural sleep pathways? It is usually assumed that anesthetic-induced sedation and loss of righting reflex (LORR) arise by influencing the same circuitry to lesser or greater extents. For the α2 adrenergic receptor agonist dexmedetomidine, we found that sedation and LORR were in fact distinct states, requiring different brain areas: the preoptic hypothalamic area and locus coeruleus (LC), respectively. Selective knockdown of α2A adrenergic receptors from the LC abolished dexmedetomidine-induced LORR, but not sedation. Instead, we found that dexmedetomidine-induced sedation resembled the deep recovery sleep that follows sleep deprivation. We used TetTag pharmacogenetics in mice to functionally mark neurons activated in the preoptic hypothalamus during dexmedetomidine-induced sedation or recovery sleep. The neuronal ensembles could then be selectively reactivated. In both cases, non-rapid eye movement sleep, with the accompanying drop in body temperature, was recapitulated. Thus, α2 adrenergic receptor-induced sedation and recovery sleep share hypothalamic circuitry sufficient for producing these behavioral states.
Figures
References
-
- Franks NP. General anaesthesia: from molecular targets to neuronal pathways of sleep and arousal. Nature reviews. Neuroscience. 2008;9:370–386. - PubMed
-
- Adams R, et al. Efficacy of dexmedetomidine compared with midazolam for sedation in adult intensive care patients: a systematic review. British journal of anaesthesia. 2013;111:703–710. - PubMed
-
- Bol C, Danhof M, Stanski DR, Mandema JW. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic characterization of the cardiovascular, hypnotic, EEG and ventilatory responses to dexmedetomidine in the rat. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 1997;283:1051–1058. - PubMed
-
- Seidel WF, Maze M, Dement WC, Edgar DM. Alpha-2 adrenergic modulation of sleep: time-of-day-dependent pharmacodynamic profiles of dexmedetomidine and clonidine in the rat. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 1995;275:263–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/F017324/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/K018159/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G021691/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT094211/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0901892/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

