The new 4-O-methylhonokiol analog GS12021 inhibits inflammation and macrophage chemotaxis: role of AMP-activated protein kinase α activation
- PMID: 25706552
- PMCID: PMC4338227
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117120
The new 4-O-methylhonokiol analog GS12021 inhibits inflammation and macrophage chemotaxis: role of AMP-activated protein kinase α activation
Abstract
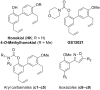
Preventing pathologic tissue inflammation is key to treating obesity-induced insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Previously, we synthesized a series of methylhonokiol analogs and reported that compounds with a carbamate structure had inhibitory function against cyclooxygenase-2 in a cell-free enzyme assay. However, whether these compounds could inhibit the expression of inflammatory genes in macrophages has not been investigated. Here, we found that a new 4-O-methylhonokiol analog, 3',5-diallyl-4'-methoxy-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl morpholine-4-carboxylate (GS12021) inhibited LPS- or TNFα-stimulated inflammation in macrophages and adipocytes, respectively. LPS-induced phosphorylation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB)/p65 was significantly decreased, whereas NF-κB luciferase activities were slightly inhibited, by GS12021 treatment in RAW 264.7 cells. Either mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation or AP-1 luciferase activity was not altered by GS12021. GS12021 increased the phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) α and the expression of sirtuin (SIRT) 1. Inhibition of mRNA expression of inflammatory genes by GS12021 was abolished in AMPKα1-knockdown cells, but not in SIRT1 knockout cells, demonstrating that GS12021 exerts anti-inflammatory effects through AMPKα activation. The transwell migration assay results showed that GS12021 treatment of macrophages prevented the cell migration promoted by incubation with conditioned medium obtained from adipocytes. GS12021 suppression of p65 phosphorylation and macrophage chemotaxis were preserved in AMPKα1-knockdown cells, indicating AMPK is not required for these functions of GS12021. Identification of this novel methylhonokiol analog could enable studies of the structure-activity relationship of this class of compounds and further evaluation of its in vivo potential for the treatment of insulin-resistant states and other chronic inflammatory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
-
- Ahn KS, Sethi G, Shishodia S, Sung B, Arbiser JL, et al. (2006) Honokiol potentiates apoptosis, suppresses osteoclastogenesis, and inhibits invasion through modulation of nuclear factor-kappaB activation pathway. Mol Cancer Res 4: 621–633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

