Napping and the selective consolidation of negative aspects of scenes
- PMID: 25706830
- PMCID: PMC5846328
- DOI: 10.1037/a0038683
Napping and the selective consolidation of negative aspects of scenes
Abstract
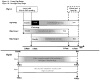
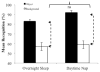
After information is encoded into memory, it undergoes an offline period of consolidation that occurs optimally during sleep. The consolidation process not only solidifies memories, but also selectively preserves aspects of experience that are emotionally salient and relevant for future use. Here, we provide evidence that an afternoon nap is sufficient to trigger preferential memory for emotional information contained in complex scenes. Selective memory for negative emotional information was enhanced after a nap compared with wakefulness in 2 control conditions designed to carefully address interference and time-of-day confounds. Although prior evidence has connected negative emotional memory formation to REM sleep physiology, we found that non-REM delta activity and the amount of slow wave sleep (SWS) in the nap were robustly related to the selective consolidation of negative information. These findings suggest that the mechanisms underlying memory consolidation benefits associated with napping and nighttime sleep are not always the same. Finally, we provide preliminary evidence that the magnitude of the emotional memory benefit conferred by sleep is equivalent following a nap and a full night of sleep, suggesting that selective emotional remembering can be economically achieved by taking a nap.
(c) 2015 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures


References
-
- Alger SE, Lau H, Fishbein W. Slow wave sleep during a daytime nap is necessary for protection from subsequent interference and long-term retention. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. 2012;98(2):188–196. - PubMed
-
- Buzsáki G. Two-stage model of memory trace formation: a role for “noisy” brain states. Neuroscience. 1989;31(3):551–570. - PubMed
-
- Buzsáki G. The hippocampo-neocortical dialogue. Cerebral Cortex. 1996;6(2):81–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

