Membrane interaction of antimicrobial peptides using E. coli lipid extract as model bacterial cell membranes and SFG spectroscopy
- PMID: 25707312
- PMCID: PMC4385500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2015.02.003
Membrane interaction of antimicrobial peptides using E. coli lipid extract as model bacterial cell membranes and SFG spectroscopy
Abstract
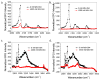
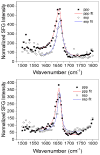
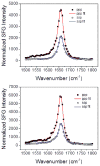
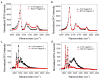
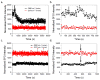
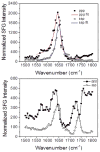
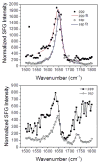
Supported lipid bilayers are used as a convenient model cell membrane system to study biologically important molecule-lipid interactions in situ. However, the lipid bilayer models are often simple and the acquired results with these models may not provide all pertinent information related to a real cell membrane. In this work, we use sum frequency generation (SFG) vibrational spectroscopy to study molecular-level interactions between the antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) MSI-594, ovispirin-1 G18, magainin 2 and a simple 1,2-dipalmitoyl-d62-sn-glycero-3-phosphoglycerol (dDPPG)/1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoglycerol (POPG) bilayer. We compared such interactions to those between the AMPs and a more complex dDPPG/Escherichia coli (E. coli) polar lipid extract bilayer. We show that to fully understand more complex aspects of peptide-bilayer interaction, such as interaction kinetics, a heterogeneous lipid composition is required, such as the E. coli polar lipid extract. The discrepancy in peptide-bilayer interaction is likely due in part to the difference in bilayer charge between the two systems since highly negative charged lipids can promote more favorable electrostatic interactions between the peptide and lipid bilayer. Results presented in this paper indicate that more complex model bilayers are needed to accurately analyze peptide-cell membrane interactions and demonstrates the importance of using an appropriate lipid composition to study AMP interaction properties.
Keywords: Antimicrobial peptide; Bacterial cell; Membrane mimetics; Peptide–lipid interactions; Sum frequency generation; Vibrational spectroscopy.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Nikaido H. Prevention of drug access to bacterial targets: Permeability barriers and active efflux. Science. 1994;264:382–388. - PubMed
-
- Bussiere DE, Muchmore SW, Dealwis CG, Schluckebier G, Nienaber VL, Edalji RP, Walter KA, Ladror US, Holzman TF, Abad-Zapatero C. Crystal structure of ErmC ‘,an rRNA methyltransferase which mediates antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Biochemistry. 1998;37:7103–7112. - PubMed
-
- Bugg TDH, Wright GD, Dutkamalen S, Arthur M, Courvalin P, Walsh CT. Molecular basis for vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus faecium BM4147: Biosynthesis of a depsipeptide peptidoglycan precursor by vancomycin resistance proteins VanH and VanA. Biochemistry. 1991;30:10408–10415. - PubMed
-
- Lambert PA. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: Modified target sites. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57:1471–1485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

