The Histone Deacetylase Sirtuin 1 Is Reduced in Systemic Sclerosis and Abrogates Fibrotic Responses by Targeting Transforming Growth Factor β Signaling
- PMID: 25707573
- PMCID: PMC4518870
- DOI: 10.1002/art.39061
The Histone Deacetylase Sirtuin 1 Is Reduced in Systemic Sclerosis and Abrogates Fibrotic Responses by Targeting Transforming Growth Factor β Signaling
Abstract
Objective: Persistent fibroblast activation underlies skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis (SSc), but the transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms controlling this process are not well understood. In view of the potent influence of acetylation status governing tissue fibrosis, we undertook this study to investigate the expression of the antiaging deacetylase enzyme sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) in SSc and its effects on fibrotic responses in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: Tissue expression of SIRTs was interrogated from publicly available genome-wide expression data sets and by immunohistochemistry. The effects of SIRT1 on modulating fibrotic responses, as well as the underlying mechanisms, were examined in human and mouse fibroblasts in culture and in an experimental fibrosis model in the mouse.
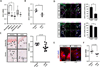
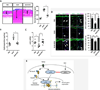
Results: Analysis of transcriptome data revealed a selective reduction of SIRT1 messenger RNA (mRNA) levels in SSc skin biopsy samples as well as a negative correlation of SIRT1 mRNA with the skin score. Cellular SIRT1 levels were suppressed in normal fibroblasts exposed to hypoxia or platelet-derived growth factor and were constitutively down-regulated in SSc fibroblasts. Activation of SIRT1 attenuated fibrotic responses in skin fibroblasts and skin organ cultures, while genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of SIRT1 had profibrotic effects. The antifibrotic effects of SIRT1 were due in part to decreased expression and function of the acetyltransferase p300. In mice, experimentally induced skin fibrosis was accompanied by reduced SIRT1 expression in lesional tissue fibroblasts, and both fibrosis and loss of SIRT1 in these mice were mitigated by treatment with a SIRT1 activator.
Conclusion: SIRT1 has antifibrotic effects, and its reduced tissue expression in patients with SSc might have a direct causal role in progression of fibrosis. Pharmacologic modulation of SIRT1 in these patients therefore might represent a potential treatment strategy.
© 2015, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
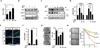
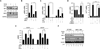

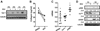
References
-
- Ghosh AK, Varga J. The transcriptional coactivator and acetyl-transferase p300 in fibroblast biology and fibrosis. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:663–671. - PubMed
-
- Mann J, Mann DA. Epigenetic regulation of wound healing and fibrosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013;25:101–107. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh AK. FAT-free p300 is good for scar-free tissue repair. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115:1486–1489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

