Semaphorin 4D Contributes to Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inducing Inflammatory Cytokine Production: Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 25707877
- PMCID: PMC5032998
- DOI: 10.1002/art.39086
Semaphorin 4D Contributes to Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inducing Inflammatory Cytokine Production: Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
Objective: Semaphorin 4D (Sema4D)/CD100 has pleiotropic roles in immune activation, angiogenesis, bone metabolism, and neural development. We undertook this study to investigate the role of Sema4D in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Soluble Sema4D (sSema4D) levels in serum and synovial fluid were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Cell surface expression and transcripts of Sema4D were analyzed in peripheral blood cells from RA patients, and immunohistochemical staining of Sema4D was performed in RA synovium. Generation of sSema4D was evaluated in an ADAMTS-4-treated monocytic cell line (THP-1 cells). The efficacy of anti-Sema4D antibody was evaluated in mice with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA).
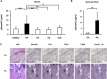
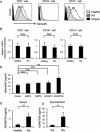
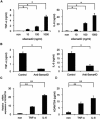
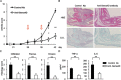
Results: Levels of sSema4D were elevated in both serum and synovial fluid from RA patients, and disease activity markers were correlated with serum sSema4D levels. Sema4D-expressing cells also accumulated in RA synovium. Cell surface levels of Sema4D on CD3+ and CD14+ cells from RA patients were reduced, although levels of Sema4D transcripts were unchanged. In addition, ADAMTS-4 cleaved cell surface Sema4D to generate sSema4D in THP-1 cells. Soluble Sema4D induced tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) production from CD14+ monocytes. IL-6 and TNFα induced ADAMTS-4 expression in synovial cells. Treatment with an anti-Sema4D antibody suppressed arthritis and reduced proinflammatory cytokine production in CIA.
Conclusion: A positive feedback loop involving sSema4D/IL-6 and TNFα/ADAMTS-4 may contribute to the pathogenesis of RA. The inhibition of arthritis by anti-Sema4D antibody suggests that Sema4D represents a potential therapeutic target for RA.
© 2015 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Semaphorin 7A as a potential immune regulator and promising therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Jan 21;19(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1217-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28109308 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 upregulates expression of ADAMTS-4 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2012 Feb;15(1):36-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2011.01656.x. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Int J Rheum Dis. 2012. PMID: 22324945
-
IL-27-producing CD14(+) cells infiltrate inflamed joints of rheumatoid arthritis and regulate inflammation and chemotactic migration.Cytokine. 2011 Aug;55(2):237-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.04.020. Epub 2011 May 17. Cytokine. 2011. PMID: 21592822
-
Soluble SEMA4D/CD100: A novel immunoregulator in infectious and inflammatory diseases.Clin Immunol. 2016 Feb;163:52-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.12.012. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26732857 Review.
-
The role of Sema4D/CD100 as a therapeutic target for tumor microenvironments and for autoimmune, neuroimmune and bone diseases.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016 Jul;20(7):885-901. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2016.1139083. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016. PMID: 26732941 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokine profiling in plasma distinguishes the histological inflammatory subtype of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and a novel regulatory role of osteopontin.Front Oral Health. 2022 Sep 12;3:993638. doi: 10.3389/froh.2022.993638. eCollection 2022. Front Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 36338570 Free PMC article.
-
CD100 modulates cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction.BMC Immunol. 2021 Feb 16;22(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12865-021-00406-y. BMC Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33593275 Free PMC article.
-
The Expression of Semaphorin3E in Vagal Ganglion and Lung Tissue Is Related to Airway Hyperresponsiveness in Murine Asthma Model.J Immunol Res. 2023 Dec 11;2023:6459234. doi: 10.1155/2023/6459234. eCollection 2023. J Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 38111650 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Semaphorins in Immunopathologies and Rheumatic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 16;20(2):374. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020374. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30654587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential role of Rnd1 in innate immunity during viral and bacterial infections.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jun 2;13(6):520. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04954-y. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35654795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kochi Y, Suzuki A, Yamamoto K. Genetic basis of rheumatoid arthritis: a current review. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014;452:254–62. - PubMed
-
- Holmdahl R, Malmstrom V, Burkhardt H. Autoimmune priming, tissue attack and chronic inflammation: the three stages of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol 2014;44:1593–9. - PubMed
-
- Ogura H, Murakami M, Okuyama Y, Tsuruoka M, Kitabayashi C, Kanamoto M, et al. Interleukin‐17 promotes autoimmunity by triggering a positive‐feedback loop via interleukin‐6 induction. Immunity 2008;29:628–36. - PubMed
-
- Zhao W, Zhang C, Shi M, Zhang J, Li M, Xue X, et al. The discoidin domain receptor 2/annexin A2/matrix metalloproteinase 13 loop promotes joint destruction in arthritis through promoting migration and invasion of fibroblast‐like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014;66:2355–67. - PubMed
-
- Cessak G, Kuzawinska O, Burda A, Lis K, Wojnar M, Mirowska‐Guzel D, et al. TNF inhibitors: mechanisms of action, approved and off‐label indications. Pharmacol Rep 2014;66:836–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

