Mitosis, microtubule dynamics and the evolution of kinesins
- PMID: 25708751
- PMCID: PMC4433793
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.02.010
Mitosis, microtubule dynamics and the evolution of kinesins
Keywords: Evolution; Evolutionary cell biology; Kinesin; LECA; Microtubule dynamics; Mitosis; Protist.
Figures

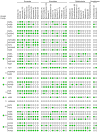
References
-
- Alsmark UC, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Foster PG, Hirt RP, Embley TM. Horizontal gene transfer in eukaryotic parasites: a case study of Entamoeba histolytica and Trichomonas vaginalis. Methods Mol Biol Clifton NJ. 2009;532:489–500. - PubMed
-
- Andersson JO. Horizontal gene transfer between microbial eukaryotes. Methods Mol Biol Clifton NJ. 2009;532:473–487. - PubMed
-
- Bar DZ. Evidence of Massive Horizontal Gene Transfer Between Humans and Plasmodium vivax. Nat Preced 2011
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

