Bioactive fraction of Saraca indica prevents diabetes induced cataractogenesis: An aldose reductase inhibitory activity
- PMID: 25709218
- PMCID: PMC4329608
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-1296.149722
Bioactive fraction of Saraca indica prevents diabetes induced cataractogenesis: An aldose reductase inhibitory activity
Abstract
Background: The present study was designed to investigate the effect of Saraca indica (SI) flowers extract and different bioactive fraction on in vitro aldose reductase (AR) inhibitory activity, high glucose-induced cataract in goat lens and in vivo streptozotocin (STZ; 45 mg/kg, i.p) induced cataract in rats.
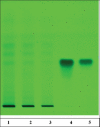
Methods: Extract of flowers of SI tested for inhibition against rat lens AR. Furthermore, bioactive fraction was investigated against high glucose-induced opacification of the lens in vitro lens culture and STZ induced diabetic cataract in rats. Identification of the bioactive component was attempted through high-performance thin-layer chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis.
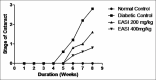
Results: Ethyl acetate fraction of S. indica (EASI) produced maximum inhibition that may be due to high phenolic content. Goat lenses in media containing glucose developed a distinctly opaque ring in 72 h and treatment with EASI fraction lowered lens opacity in 72 h. Prolonged treatment with EASI to STZ-induced diabetic rats inhibited the AR activity and delayed cataract progression in a dose dependent manner.
Conclusion: Ethyl acetate fraction of S. indica fraction has potential to inhibit rat lens AR enzyme and prevent cataractogenesis not only in goat lens model (in vitro), but also in STZ induced diabetic rats (in vivo). This study is suggestive of the anticataract activity of EASI fraction that could be attributed to the phytoconstituents present in the same.
Keywords: Cataractogenesis; Saraca indica; streptozotocin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Thymol, a monoterpene, inhibits aldose reductase and high-glucose-induced cataract on isolated goat lens.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2016 Oct-Dec;8(4):277-283. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.199348. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2016. PMID: 28216950 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of aldose reductase by Aegle marmelos and its protective role in diabetic cataract.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Aug 26;149(1):215-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.025. Epub 2013 Jul 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23827758
-
Water extract of Aralia elata prevents cataractogenesis in vitro and in vivo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2005 Oct 3;101(1-3):49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.03.020. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15905053
-
Lens aldose reductase inhibiting potential of some indigenous plants.J Ethnopharmacol. 2003 May;86(1):113-6. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(03)00052-7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12686449
-
Protective effect of Tephrosia purpurea in diabetic cataract through aldose reductase inhibitory activity.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Oct;83:221-228. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.05.018. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27372406
Cited by
-
Astragalin attenuates diabetic cataracts via inhibiting aldose reductase activity in rats.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Aug 18;16(8):1186-1195. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.08.02. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37602342 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating potent cardioprotective compounds as ACE inhibitors in Saraca asoca.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Sep 10;13:101731. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101731. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39309635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymol, a monoterpene, inhibits aldose reductase and high-glucose-induced cataract on isolated goat lens.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2016 Oct-Dec;8(4):277-283. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.199348. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2016. PMID: 28216950 Free PMC article.
-
Resolving Identification Issues of Saraca asoca from Its Adulterant and Commercial Samples Using Phytochemical Markers.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jul;13(Suppl 2):S266-S272. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_417_16. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 28808391 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of Polyol Pathway Activity by Hemidesmus indicus var. pubescens R.Br. Linn Root Extract, an Aldose Reductase Inhibitor: An In Silico and Ex Vivo Study.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2021 Jun;11(3):315-324. doi: 10.1007/s13659-020-00290-w. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2021. PMID: 33284412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Congdon NG, Friedman DS, Lietman T. Important causes of visual impairment in the world today. JAMA. 2003;290:2057–60. - PubMed
-
- Kinoshita JH. A thirty year journey in the polyol pathway. Exp Eye Res. 1990;50:567–73. - PubMed
-
- Yabe-Nishimura C. Aldose reductase in glucose toxicity: A potential target for the prevention of diabetic complications. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:21–33. - PubMed
-
- Chatzopoulou M, Alexiou P, Kotsampasakou E, Demopoulos VJ. Novel aldose reductase inhibitors: A patent survey (2006 – present) Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2012;22:1303–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
