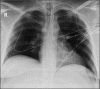
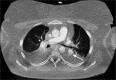
Salvage intraosseous thrombolysis and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for massive pulmonary embolism
- PMID: 25709256
- PMCID: PMC4335161
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2700.145395
Salvage intraosseous thrombolysis and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for massive pulmonary embolism
Abstract
Intraosseous access is an alternative route of pharmacotherapy during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) provides cardiac and respiratory support when conventional therapies fail. This case reports the use of intraosseous thrombolysis and ECMO in a patient with acute massive pulmonary embolism (PE). A 34-year-old female presented to the emergency department with sudden onset severe shortness of breath. Due to difficulty establishing intravenous access, an intraosseous needle was inserted into the left tibia. Echocardiography identified severe right ventricular dilatation with global systolic impairment and failure, indicative of PE. Due to the patient's hemodynamic compromise a recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (Alteplase) bolus was administered through the intraosseous route. After transfer to the intensive care unit, venous-arterial ECMO was initiated as further therapy. The patient recovered and was discharged 36 days after admission. This is the first report of combination intraosseous thrombolysis and ECMO as salvage therapy for massive PE.
Keywords: Cardiac arrest; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; intraosseous; pulmonary embolism; thrombolytic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Successful Intraosseous Thrombolysis in the Management of a Massive Pulmonary Embolism With Cardiac Arrest.Cureus. 2020 Dec 16;12(12):e12105. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12105. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33489522 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple boluses of alteplase followed by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for massive pulmonary embolism.Am J Emerg Med. 2019 Sep;37(9):1808.e5-1808.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2019.06.029. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Am J Emerg Med. 2019. PMID: 31253518
-
Successful use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for pulmonary embolism, prolonged cardiac arrest, post-partum: a cannulation dilemma.Perfusion. 2015 Mar;30(2):106-10. doi: 10.1177/0267659114555818. Epub 2014 Oct 10. Perfusion. 2015. PMID: 25304130
-
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in acute massive pulmonary embolism: a case series and review of the literature.Perfusion. 2019 Jan;34(1):22-28. doi: 10.1177/0267659118786830. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Perfusion. 2019. PMID: 30009670 Review.
-
Massive Pulmonary Embolism: Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation and Surgical Pulmonary Embolectomy.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2017 Feb;38(1):66-72. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1597559. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 28208200 Review.
Cited by
-
A rare complication of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and thrombolytic treatment in a patient with massive pulmonary embolism: Intraperitoneal hemorrhage.Turk J Emerg Med. 2020 Dec 1;21(1):34-37. doi: 10.4103/2452-2473.301916. eCollection 2021 Jan-Mar. Turk J Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 33575514 Free PMC article.
-
Negative Outcome Following Systemic Alteplase Administration Prior to Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in a Kidney Transplant Patient With Cardiac Arrest: A Case Report.J Clin Med Res. 2022 Jul;14(7):282-286. doi: 10.14740/jocmr4744. Epub 2022 Jul 29. J Clin Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35974803 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes in Cardiogenic Shock Patients with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Use: A Matched Cohort Study in Hospitals across the United States.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jan 22;2018:2428648. doi: 10.1155/2018/2428648. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29789779 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiography for patients undergoing extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a primer for intensive care physicians.J Intensive Care. 2017 Feb 2;5:15. doi: 10.1186/s40560-017-0211-6. eCollection 2017. J Intensive Care. 2017. PMID: 28168038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) for critically ill adults in the emergency department: history, current applications, and future directions.Crit Care. 2015 Dec 17;19:431. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-1155-7. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 26672979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaff MR, McMurtry MS, Archer SL, Cushman M, Goldenberg N, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis, and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011;123:1788–830. - PubMed
-
- Valdés M, Araujo P, de Andrés C, Sastre E, Martin T. Intraosseous administration of thrombolysis in out-of-hospital massive pulmonary thromboembolism. Emerg Med J. 2010;27:641–4. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz-Hornillos PJ, Martínez-Cámara F, Elizondo M, Jiménez-Fraile JA, Del Mar Alonso-Sánchez M, Galán D, et al. Systemic fibrinolysis through intraosseous vascular access in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57:572–4. - PubMed
-
- Landy C, Plancade D, Gagnon N, Schaeffer E, Nadaud J, Favier JC. Complication of intraosseous administration of systemic fibrinolysis for a massive pulmonary embolism with cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2012;83:e149–50. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources