Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular function in thyrotoxicosis and implications for the therapeutics of thyrotoxic cardiac disease
- PMID: 25709461
- PMCID: PMC4332259
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S68752
Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular function in thyrotoxicosis and implications for the therapeutics of thyrotoxic cardiac disease
Abstract
Introduction: Thyrotoxicosis is an endocrine disorder with prominent cardiovascular manifestations. Thyroid hormone acts through genomic and non-genomic mechanisms to regulate cardiac function. Echocardiography is a useful, non-invasive, easily accessible, and affordable tool for studying the structural and physiological function of the heart.
Aim: We studied thyrotoxicosis patients in a Nigerian Teaching Hospital and employed trans-thoracic echocardiography to find out if there were abnormalities in the hearts of these patients.
Methods: Fifty adult thyrotoxicosis patients diagnosed with clinical and thyroid function tests in the medical out-patient unit of the hospital were recruited and we performed transthoracic echocardiography with a Sonos 2000 HP machine.
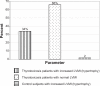
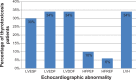
Results: We documented the presence of abnormalities in the following proportion of thyrotoxicosis patients: left ventricular enhanced systolic function in 30%, enhanced diastolic function in 34%, diastolic dysfunction in 34%, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in10%, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction in 6%, and left ventricular hypertrophy in 34%.
Conclusion: Echocardiography was useful in the stratification of cardiac function abnormalities and is indispensable as a guide in the choice of therapeutic options in patients with thyrocardiac disease. The finding of left ventricular enhanced systolic and diastolic functions signify early echocardiographic detectable cardiac abnormalities in thyrotoxicosis, and the clinical management includes the use of anti-thyroid drugs and β-adrenoceptor blockade. Diastolic dysfunction in thyrotoxicosis patients asymptomatic for cardiac disease should be treated with anti-thyroid drugs, and β-adrenoceptor blockade. The judicious application of clinical therapeutics will guide the use of anti-thyroid drugs, diuretics, digoxin, angiotensin inhibitors, and β-adrenoceptor blockade in the successful management of thyrotoxicosis patients with heart failure and reduced, preserved, or increased ejection fraction: parameters which are derived from echocardiography.
Keywords: echocardiography; left ventricle; therapeutics; thyrocardiac disease; thyrotoxicosis.
Figures
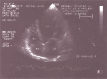
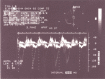
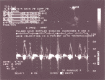
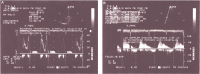
References
-
- Gordon HW, Leonard SL, Ellen WS. The heart in endocrine and nutritional disorders. In: Braunwald E, editor. Heart Disease. 5th ed. Philadelphia: W B Saunders; 1997. pp. 1890–1894.
-
- Weetman AP. Grave’s disease 1835–2002. Horm Res. 2003;59(Suppl 1):114–118. - PubMed
-
- Kahaly GJ, Dillmann WH. Thyroid hormone action in the heart. Endocrine Rev. 2005;26(5):704–728. - PubMed
-
- Kiss E, Jakab G, Kranias EG, Edes I. Thyroid hormone-induced alterations in phospholamban protein expression: regulatory effects on sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transport and myocardial relaxation. Circ Res. 1994;75(2):245–251. - PubMed
-
- Klein I, Ojamaa K. Thyroid hormone and the cardiovascular system. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(7):501–509. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

