Radiosynovectomy in the therapeutic management of arthritis
- PMID: 25709538
- PMCID: PMC4337000
- DOI: 10.4103/1450-1147.150509
Radiosynovectomy in the therapeutic management of arthritis
Abstract
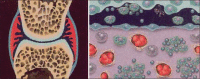
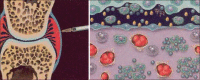
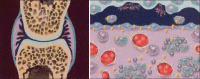
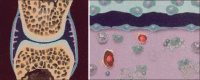
Radiosynovectomy is a well-established therapy in arthritis and involves an intra-articular injection of small radioactive particles to treat a synovitis. In Europe, frequent indications are rheumatoid and poly-arthritis. Especially in Germany radiosynovectomy is the second common therapy in Nuclear Medicine with about 40,000-60,000 treated joints per year. In Spain, USA, Turkey, Argentines and Philippines the therapy is more use in hemophilic arthritis with excellent results. Especially in developing countries with low availability of clotting factors, the radiosynovectomy represent a cost effective therapeutic option for repeated bleedings in hemophilic arthropathy. The special focus in these countries is maintaining of mobility and work ability. Often only the knee and medium joints (ankle, elbow and shoulder) are treated using yttrium-90, rhenium-186 or phosphorus-32. However, in rheumatoid arthritis most common affected joints are the fingers. For the treatment in these small joints, erbium-169 is necessary. Unfortunately, erbium-169 is only available in Europe. Further indications for radiosynovectomy are osteoarthritis and the articular effusion after joint replacement. The reported response rates in rheumatoid and poly-arthritis range from 60% to 80% depends from the stage of previous arthrosis. The best effectiveness of therapy was observed in hemophilic arthritis with response rate of 90% and significant reducing of bleeding frequency. The therapy is well-tolerated with low rate of side effects. In respect of the specific uptake of particles in the synovia and short range of beta radiation, the radiation exposure outside the joint is very low. The radiosynovectomy has efforts in comparison to surgical synovectomy: it's a minor intervention with low costs; and simultaneous treatments of multiple joints or treatment in short intervals are possible. The presented paper summarized the published papers and reports our own experiences in >15,000 treated joints.
Keywords: Erbium-169; hemophilic arthritis; osteoarthritis; rhenium-186; rheumatoid arthritis; yttrium-90.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
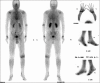
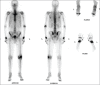
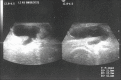

References
-
- Liepe K, Zaknun JJ, Padhy A, Barrenechea E, Soroa V, Shrikant S, et al. Radiosynovectomy using yttrium-90, phosphorus-32 or rhenium-188 radiocolloids versus corticoid instillation for rheumatoid arthritis of the knee. Ann Nucl Med. 2011;25:317–23. - PubMed
-
- Soroa VE, del Huerto Velázquez Espeche M, Giannone C, Caviglia H, Galatros G, Fernández D, et al. Effects of radiosynovectomy with p-32 colloid therapy in hemophilia and rheumatoid arthritis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2005;20:344–8. - PubMed
-
- Bessant R, Steuer A, Rigby S, Gumpel M. Osmic acid revisited: Factors that predict a favourable response. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003;42:1036–43. - PubMed
-
- Kerschbaumer F, Bauer R, Falser N, Altmann H. Effects and side effects of radiosynovectomy with Yttrium 90 on rheumatic joint cartilage. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1979;93:95–102. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

