Training spiking neural models using artificial bee colony
- PMID: 25709644
- PMCID: PMC4331474
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/947098
Training spiking neural models using artificial bee colony
Abstract
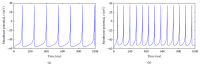
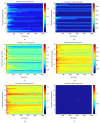
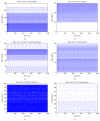
Spiking neurons are models designed to simulate, in a realistic manner, the behavior of biological neurons. Recently, it has been proven that this type of neurons can be applied to solve pattern recognition problems with great efficiency. However, the lack of learning strategies for training these models do not allow to use them in several pattern recognition problems. On the other hand, several bioinspired algorithms have been proposed in the last years for solving a broad range of optimization problems, including those related to the field of artificial neural networks (ANNs). Artificial bee colony (ABC) is a novel algorithm based on the behavior of bees in the task of exploring their environment to find a food source. In this paper, we describe how the ABC algorithm can be used as a learning strategy to train a spiking neuron aiming to solve pattern recognition problems. Finally, the proposed approach is tested on several pattern recognition problems. It is important to remark that to realize the powerfulness of this type of model only one neuron will be used. In addition, we analyze how the performance of these models is improved using this kind of learning strategy.
Figures


References
-
- Garro B. A., Sossa H., Vazquez R. A. Design of artificial neural networks using a modified particle swarm optimization algorithm. Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN '09); June 2009; pp. 938–945. - DOI
-
- Garro B. A., Sossa H., Vázquez R. A. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Neural Information Processing: Models and Applications—Part II (ICONIP '10) Vol. 6444. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2010. Design of artificial neural networks using differential evolution algorithm; pp. 201–208. (Lecture Notes in Computer Science).
-
- Dorigo M., Blum C. Ant colony optimization theory: a survey. Theoretical Computer Science. 2005;344(2-3):243–278. doi: 10.1016/j.tcs.2005.05.020. - DOI
-
- Karaboga D., Basturk B. A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. Journal of Global Optimization. 2007;39(3):459–471. doi: 10.1007/s10898-007-9149-x. - DOI
-
- Karaboga D., Gorkemli B., Ozturk C., Karaboga N. A comprehensive survey: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm and applications. Artificial Intelligence Review. 2014;42(1):21–57. doi: 10.1007/s10462-012-9328-0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

