Facial nerve trauma: evaluation and considerations in management
- PMID: 25709748
- PMCID: PMC4329040
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1372522
Facial nerve trauma: evaluation and considerations in management
Abstract
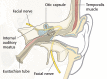
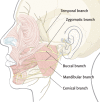
The management of facial paralysis continues to evolve. Understanding the facial nerve anatomy and the different methods of evaluating the degree of facial nerve injury are crucial for successful management. When the facial nerve is transected, direct coaptation leads to the best outcome, followed by interpositional nerve grafting. In cases where motor end plates are still intact but a primary repair or graft is not feasible, a nerve transfer should be employed. When complete muscle atrophy has occurred, regional muscle transfer or free flap reconstruction is an option. When dynamic reanimation cannot be undertaken, static procedures offer some benefit. Adjunctive tools such as botulinum toxin injection and biofeedback can be helpful. Several new treatment modalities lie on the horizon which hold potential to alter the current treatment algorithm.
Keywords: facial nerve injury; facial paralysis rehabilitation; facial reanimation; facial sling; free tissue transfer; hypoglossal-facial nerve transfer; intratemporal facial nerve trauma; temporalis tendon transposition.
Figures
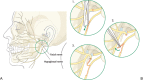
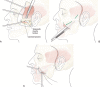
References
-
- May M. New York, NY: Thieme Medical Publishers; 2000. Anatomy for the clinician; pp. 19–56.
-
- Bernstein L, Nelson R. Surgical anatomy of the extraparotid distribution of the facial nerve. Arch Otolaryngol. 1984;110:177–183. - PubMed
-
- Tate J, Tollefson T. Advances in facial reanimation. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;14:242–248. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron C, Moe K. The evaluation and treatment of upper eyelid paralysis. Facial Plast Surg. 2008;24(2):220–230. - PubMed
-
- Meltzer N E, Alam D S. Facial paralysis rehabilitation: state of the art. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;18(4):232–237. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
