Big data challenges in bone research: genome-wide association studies and next-generation sequencing
- PMID: 25709812
- PMCID: PMC4325556
- DOI: 10.1038/bonekey.2015.2
Big data challenges in bone research: genome-wide association studies and next-generation sequencing
Abstract
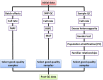
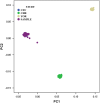
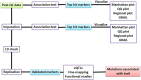
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have been developed as a practical method to identify genetic loci associated with disease by scanning multiple markers across the genome. Significant advances in the genetics of complex diseases have been made owing to advances in genotyping technologies, the progress of projects such as HapMap and 1000G and the emergence of genetics as a collaborative discipline. Because of its great potential to be used in parallel by multiple collaborators, it is important to adhere to strict protocols assuring data quality and analyses. Quality control analyses must be applied to each sample and each single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). The software package PLINK is capable of performing the whole range of necessary quality control tests. Genotype imputation has also been developed to substantially increase the power of GWAS methodology. Imputation permits the investigation of associations at genetic markers that are not directly genotyped. Results of individual GWAS reports can be combined through meta-analysis. Finally, next-generation sequencing (NGS) has gained popularity in recent years through its capacity to analyse a much greater number of markers across the genome. Although NGS platforms are capable of examining a higher number of SNPs compared with GWA studies, the results obtained by NGS require careful interpretation, as their biological correlation is incompletely understood. In this article, we will discuss the basic features of such protocols.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Gavin Lucas is a partner in Clear Genetics. Dr Nerea Alonso and Dr Pirro Hysi declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extending the use of GWAS data by combining data from different genetic platforms.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 28;12(2):e0172082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172082. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28245255 Free PMC article.
-
Use of genotyping-by-sequencing to determine the genetic structure in the medicinal plant chamomile, and to identify flowering time and alpha-bisabolol associated SNP-loci by genome-wide association mapping.BMC Genomics. 2017 Aug 10;18(1):599. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3991-0. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28797221 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of HapMap and 1000 Genomes Reference Panels in a Large-Scale Genome-Wide Association Study.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 20;12(1):e0167742. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167742. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28107422 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype Imputation in Genome-Wide Association Studies.Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2019 Jun;102(1):e84. doi: 10.1002/cphg.84. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31216114 Review.
-
Recommendations for Choosing the Genotyping Method and Best Practices for Quality Control in Crop Genome-Wide Association Studies.Front Genet. 2020 Jun 5;11:447. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00447. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32587600 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-Throughput Sequencing to Investigate Associations Between HLA Genes and Metamizole-Induced Agranulocytosis.Front Genet. 2020 Aug 21;11:951. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00951. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32973882 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study of Metamizole-Induced Agranulocytosis in European Populations.Genes (Basel). 2020 Oct 29;11(11):1275. doi: 10.3390/genes11111275. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33138277 Free PMC article.
-
Studying the effects of haplotype partitioning methods on the RA-associated genomic results from the North American Rheumatoid Arthritis Consortium (NARAC) dataset.J Adv Res. 2019 Jan 18;18:113-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2019.01.006. eCollection 2019 Jul. J Adv Res. 2019. PMID: 30891314 Free PMC article.
-
Independent and Combined Associations of Sleep Duration, Bedtime, and Polygenic Risk Score with the Risk of Hearing Loss among Middle-Aged and Old Chinese: The Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort Study.Research (Wash D C). 2023 Jun 27;6:0178. doi: 10.34133/research.0178. eCollection 2023. Research (Wash D C). 2023. PMID: 37383219 Free PMC article.
-
A Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies a Candidate Gene Associated With Atazanavir Exposure Measured in Hair.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Nov;104(5):949-956. doi: 10.1002/cpt.1014. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29315502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olivier M. A haplotype map of the human genome. Physiol Genomics 2003;13:3–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
