Combined 23-gauge sutureless vitrectomy and clear corneal phacoemulsification for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment repair
- PMID: 25709921
- PMCID: PMC4325255
- DOI: 10.3980/J.ISSN.2222-3959.2015.01.23
Combined 23-gauge sutureless vitrectomy and clear corneal phacoemulsification for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment repair
Abstract
Aim: To assess the outcomes of combined 23-gauge sutureless vitrectomy and clear corneal phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) repair.
Methods: This was a retrospective, consecutive, non-comparative, interventional case series of 30 eyes of 30 patients who underwent combined sutureless vitrectomy and clear corneal cataract surgery for the repair of RRD. The principal outcome measures were primary anatomical success rate, reasons for redetachment, final visual acuity, and surgical complications.
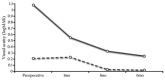
Results: Primary reattachment was achieved in 27 eyes (90.0%). The reasons for redetachment (3 eyes, 10%) were incomplete laser retinopexy, persistent chronic subretinal fluid, and proliferative vitreoretinopathy, respectively. The logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution visual acuity (mean±SD) improved from 0.76±0.74 preoperatively to 0.21±0.37 6 months' postoperatively (P<0.0001). Postoperative hypotony was not detected, but 1 eye (3.3%) had increased intraocular pressure (30mmHg) with spontaneous resolution. No endophthalmitis developed during follow-up. Macular pucker was detected in 3 eyes (10.0%).
Conclusion: Combined 23-gauge sutureless vitrectomy and clear corneal phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation for RRD repair was proven safe and effective. It may provide not only the known advantages of conventional combined surgery, but also additional advantages such as less conjunctival fibrosis and the maintenance of stable intraocular pressure with low risks of postoperative hypotony and intraocular pressure elevation.
Keywords: clear corneal phacoemulsification; combined 23-guage sutureless vitrectomy; rhegmatogenous retinal detachment.
Figures
References
-
- Fujii GY, De Juan E, Jr, Humayun MS, Chang TS, Pieramici DJ, Barnes A, Kent D. Initial experience using the transconjunctival sutureless vitrectomy system for vitreoretinal surgery. Ophthalmology. 2002;109(10):1814–1820. - PubMed
-
- Fujii GY, De Juan E, Jr, Humayun MS, Pieramici DJ, Chang TS, Awh C, Ng E, Barnes A, Wu SL, Sommerville DN. A new 25-gauge instrument system for transconjunctival sutureless vitrectomy surgery. Ophthalmology. 2002;109(10):1807–1812. - PubMed
-
- Eckardt C. Transconjunctival sutureless 23-gauge vitrectomy. Retina. 2005;25(2):208–211. - PubMed
-
- Lai MM, Ruby AJ, Sarrafizadeh R, Urban KE, Hassan TS, Drenser KA, Garretson BR. Repair of primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment using 25-gauge transconjunctival sutureless vitrectomy. Retina. 2008;28(5):729–734. - PubMed
-
- Tsang CW, Cheung BT, Lam RF, Lee GK, Yuen CY, Lai TY, Lam DS. Primary 23-gauge transconjunctival sutureless vitrectomy for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Retina. 2008;28(8):1075–1081. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources