Using Markov Chains to predict the natural progression of diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 25709923
- PMCID: PMC4325257
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2015.01.25
Using Markov Chains to predict the natural progression of diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
Aim: To study the natural progression of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods: This was an observational study of 153 cases with type 2 diabetes from 2010 to 2013. The state of patient was noted at end of each year and transition matrices were developed to model movement between years. Patients who progressed to severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) were treated. Markov Chains and Chi-square test were used for statistical analysis.
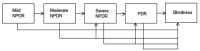
Results: We modelled the transition of 153 patients from NPDR to blindness on an annual basis. At the end of year 3, we compared results from the Markov model versus actual data. The results from Chi-square test confirmed that there was statistically no significant difference (P=0.70) which provided assurance that the model was robust to estimate mean sojourn times. The key finding was that a patient entering the system in mild NPDR state is expected to stay in that state for 5y followed by 1.07y in moderate NPDR, be in the severe NPDR state for 1.33y before moving into PDR for roughly 8y. It is therefore expected that such a patient entering the model in a state of mild NPDR will enter blindness after 15.29y.
Conclusion: Patients stay for long time periods in mild NPDR before transitioning into moderate NPDR. However, they move rapidly from moderate NPDR to proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) and stay in that state for long periods before transitioning into blindness.
Keywords: Chi-square test; Markov Chains; diabetes mellitus; diabetic retinopathy; transition probability matrix.
Figures
References
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Frick DK, Gower EW, Kempen HJ, Wolff LJ. Economic impact of visual impairment and blindness in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol. 2007;125(4):544–550. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources