Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationships and docking studies of some structurally diverse flavonoids and design of new aldose reductase inhibitors
- PMID: 25709964
- PMCID: PMC4330605
- DOI: 10.4103/2231-4040.150366
Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationships and docking studies of some structurally diverse flavonoids and design of new aldose reductase inhibitors
Abstract
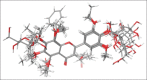
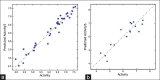
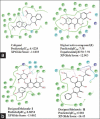
Aldose reductase (AR) plays an important role in the development of several long-term diabetic complications. Inhibition of AR activities is a strategy for controlling complications arising from chronic diabetes. Several AR inhibitors have been reported in the literature. Flavonoid type compounds are shown to have significant AR inhibition. The objective of this study was to perform a computational work to get an idea about structural insight of flavonoid type compounds for developing as well as for searching new flavonoid based AR inhibitors. The data-set comprising 68 flavones along with their pIC50 values ranging from 0.44 to 4.59 have been collected from literature. Structure of all the flavonoids were drawn in Chembiodraw Ultra 11.0, converted into corresponding three-dimensional structure, saved as mole file and then imported to maestro project table. Imported ligands were prepared using LigPrep option of maestro 9.6 version. Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationships and docking studies were performed with appropriate options of maestro 9.6 version installed in HP Z820 workstation with CentOS 6.3 (Linux). A model with partial least squares factor 5, standard deviation 0.2482, R(2) = 0.9502 and variance ratio of regression 122 has been found as the best statistical model.
Keywords: Aldose reductase; designed inhibitor; extra precision glide docking; flavonoids; three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationships.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




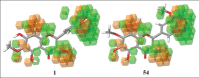
Similar articles
-
Kinetics and molecular docking studies of kaempferol and its prenylated derivatives as aldose reductase inhibitors.Chem Biol Interact. 2012 May 30;197(2-3):110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2012.04.004. Epub 2012 Apr 21. Chem Biol Interact. 2012. PMID: 22543015
-
Protective effect of Tephrosia purpurea in diabetic cataract through aldose reductase inhibitory activity.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Oct;83:221-228. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.05.018. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27372406
-
Synthesis of flavonoids and their effects on aldose reductase and sorbitol accumulation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat tissues.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2001 May;53(5):653-68. doi: 10.1211/0022357011775983. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11370705
-
Potential use of aldose reductase inhibitors to prevent diabetic complications.Clin Pharm. 1990 Jun;9(6):446-57. Clin Pharm. 1990. PMID: 2114249 Review.
-
Aldose reductase inhibitors from the nature.Curr Med Chem. 2003 Aug;10(15):1353-74. doi: 10.2174/0929867033457304. Curr Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12871134 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms Provide a Landscape for Biomarker Selection for Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Psychosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 18;24(20):15296. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015296. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001;414:782–7. - PubMed
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas Sixth Edition Poster Update 2014. Available from: http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas/update-2014 .
-
- Gabbay KH, Merola LO, Field RA. Sorbitol pathway: Presence in nerve and cord with substrate accumulation in diabetes. Science. 1966;151:209–10. - PubMed
-
- Lindstad RI, McKinley-McKee JS. Methylglyoxal and the polyol pathway. Three-carbon compounds are substrates for sheep liver sorbitol dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1993;330:31–5. - PubMed
-
- Gabbay KH, O'Sullivan JB. The sorbitol pathway. Enzyme localization and content in normal and diabetic nerve and cord. Diabetes. 1968;17:239–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
