Geranisetron versus gabapentin in preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting after middle ear surgery in adults: A double-blinded randomized clinical trial study
- PMID: 25709987
- PMCID: PMC4333427
- DOI: 10.4103/2277-9175.150388
Geranisetron versus gabapentin in preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting after middle ear surgery in adults: A double-blinded randomized clinical trial study
Abstract
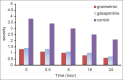
Background: The incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) after middle ear surgery is high. In this study we want to compare the effects of intravenous granisetron and oral gabapentin as a premedication before surgery on the incidence and severity of PONV after middle ear surgery in adult patents.
Materials and methods: We enrolled 90 patients that were randomly divided into the three groups of 30 in each. Group I received granisetron 3 mg iv 2 minutes before induction of anesthesia; Group II received oral gabapentin 300 mg 1 hour before anesthesia and Group III received placebo. The incidence and severity of PONV were recorded each 15 minutes in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) and each 8 hours until 24 hours after discharge from the PACU.
Result: The incidence and severity of nausea and vomiting at different time intervals in Groups I and Group II was significantly lower compared with Group III (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the incidence of side effects of study drug administration including respiratory depression, apnea, extra pyramidal disorders, drowsiness, dizziness, vertigo and headache in three groups.
Conclusion: The study was shown that using gabapentin and granisetron have equal anti-emetic effects, but significant differences were seen between these two groups compared to the control group. These submit the efficiency of these drugs in preventing PONV.
Keywords: 5HT3 receptors; American social anesthesia; gabapentin; geranisetrone; post operating nausea and vomiting (PONV); visual analogues scale.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Miller RD. Anesthesia. In: Fleisher LA, Macario A, editors. The postanesthesia care unit. 6th ed. Pennsylvania: Elsevier; 2010. pp. 2703–27.
-
- Habib AS, Gan TJ. Evidence-based management of postoperative nausea and vomiting: A review. Can J Anesth. 2004;51:326–41. - PubMed
-
- Splinter WM, MacNeill HB, Menard EA, Rhine EJ, Roberts DJ, Gould MH. Midazolam reduces vomiting after tonsillectomy in children. Can J Anaesth. 1995;42:201–3. - PubMed
-
- Korttila K, Alahuhta S, Ali-Melkkila DT, Tarkkila DP, Hynynen DM. Prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting-studies on different antiemetics, their combinations and dosing regimens. Biomedicum Helsinki. 2003;26:1–78.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources