Utility of circulating microRNAs as clinical biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 25710029
- PMCID: PMC4330947
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/821823
Utility of circulating microRNAs as clinical biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
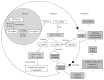
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNA molecules that regulate gene and protein expression by translational repression and/or mRNA degradation. miRNAs are implicated in the pathogenesis of various cardiovascular diseases and have become potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Their stability and presence in variety of readily accessible cell types including whole blood, serum, plasma, and other body fluids render them as potential source of a clinical biomarker. This review provides a brief overview of miRNA biogenesis and function, the diagnostic potential of circulating extracellular miRNA and their specific role in vivo in various cardiovascular settings, and their future perspective as clinical biomarkers. It is clearly evident from experimental studies that miRNAs are responsible for the regulation of several biological functions and alterations in cardiovascular diseases. Current data supports the concept of using circulating miRNAs as a biomarker in cardiovascular disease. It remains to be seen, however, whether circulating miRNAs can fulfil this role to improve risk and severity prediction.
Figures
References
-
- Rosamond W., Flegal K., Furie K., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2008 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2008;117(4):e25–e146. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones D., Adams R. J., Brown T. M. Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics—2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121(7):948–954. - PubMed
-
- Pearson T. A., Mensah G. A., Alexander R. W., et al. Markers of inflammation and cardiovascular disease: application to clinical and public health practice: A statement for healthcare professionals from the centers for disease control and prevention and the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2003;107(3):499–511. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000052939.59093.45. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

