In vitro inhibitory and cytotoxic activity of MFM 501, a novel codonopsinine derivative, against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates
- PMID: 25710030
- PMCID: PMC4331153
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/823829
In vitro inhibitory and cytotoxic activity of MFM 501, a novel codonopsinine derivative, against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates
Abstract
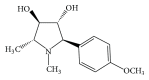
28 new pyrrolidine types of compounds as analogues for natural polyhydroxy alkaloids of codonopsinine were evaluated for their anti-MRSA activity using MIC and MBC value determination assay against a panel of S. aureus isolates. One pyrrolidine compound, MFM 501, exhibited good inhibitory activity with MIC value of 15.6 to 31.3 μg/mL against 55 S. aureus isolates (43 MRSA and 12 MSSA isolates). The active compound also displayed MBC values between 250 and 500 μg/mL against 58 S. aureus isolates (45 MRSA and 13 MSSA isolates) implying that MFM 501 has a bacteriostatic rather than bactericidal effect against both MRSA and MSSA isolates. In addition, MFM 501 showed no apparent cytotoxicity activity towards three normal cell lines (WRL-68, Vero, and 3T3) with IC50 values of >625 µg/mL. Selectivity index (SI) of MFM 501 gave a value of >10 suggesting that MFM 501 is significant and suitable for further in vivo investigations. These results suggested that synthetically derived intermediate compounds based on natural products may play an important role in the discovery of new anti-infective agents against MRSA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[In vitro activity of ceftaroline against Spanish isolates of Staphylococcus aureus: a multicenter study].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2015 Feb;33(2):101-4. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Aug 3. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2015. PMID: 25091384 Spanish.
-
In vitro activity of retapamulin against linezolid and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates.Rev Esp Quimioter. 2011 Sep;24(3):127-30. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2011. PMID: 21947094
-
Telavancin demonstrates activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin, daptomycin, and linezolid in broth microdilution MIC and one-compartment pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic models.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Sep;59(9):5529-34. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00773-15. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26124162 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacodynamic activity of ceftobiprole compared with vancomycin versus methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) using an in vitro model.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009 Aug;64(2):364-9. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp176. Epub 2009 May 19. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19454524
-
In vitro synergism of magnolol and honokiol in combination with antibacterial agents against clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Dec 1;15:425. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0938-3. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26627468 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Amino acid-derived defense metabolites from plants: A potential source to facilitate novel antimicrobial development.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100438. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100438. Epub 2021 Feb 19. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33610552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereoselective Chemoenzymatic Cascades for the Synthesis of Densely Functionalized Iminosugars.J Am Chem Soc. 2025 Feb 19;147(7):6067-6075. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c16732. Epub 2025 Feb 10. J Am Chem Soc. 2025. PMID: 39925122 Free PMC article.
-
Total syntheses of codonopsinine and 4-epi-codonopsinine via gold-mediated tandem-catalyzed pyrrole synthesis.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2016 Apr;69(4):253-8. doi: 10.1038/ja.2016.13. Epub 2016 Feb 17. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2016. PMID: 26883393
-
The Role of Five-Membered Heterocycles in the Molecular Structure of Antibacterial Drugs Used in Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Oct 29;15(11):2554. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112554. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38004534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Evaluations and In Vivo Toxicity and Efficacy Studies of MFM501 against MRSA.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:8032865. doi: 10.1155/2017/8032865. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28536702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sameerah S. A. R. Pattern of antibiotic usage in MOH hospitals. Proceedings of the New Strategies in Combating Anti-Infectives Resistance Seminar; October 2009; Melaka, Malaysia. Keynote;
-
- Lailatul A. Introduction: antibiotic resistance in Malaysia. Keynote Presentation at the New Strategies in Combating Anti- Infectives Resistance Seminar; October 2009; Melaka, Malaysia;
-
- Ramli S. R., Neoh H.-M., Aziz M. N., Hussin S. Screening and detection of heterogenous vancomycin intermediate Staphylococcus aureus in Hospital Kuala Lumpur Malaysia, using the glycopeptide resistance detection Etest and population analysis profiling. Infectious Disease Reports. 2012;4(1):71–72. doi: 10.4081/idr.2012.e20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad N., Ling L. N., Ghani M. K. A., Nawi S. The presence of heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (heteroVISA) in a major Malaysian hospital. Medical Journal of Malaysia. 2012;67(3):269–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases