Recalibration of the limiting antigen avidity EIA to determine mean duration of recent infection in divergent HIV-1 subtypes
- PMID: 25710171
- PMCID: PMC4339840
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114947
Recalibration of the limiting antigen avidity EIA to determine mean duration of recent infection in divergent HIV-1 subtypes
Abstract
Background: Mean duration of recent infection (MDRI) and misclassification of long-term HIV-1 infections, as proportion false recent (PFR), are critical parameters for laboratory-based assays for estimating HIV-1 incidence. Recent review of the data by us and others indicated that MDRI of LAg-Avidity EIA estimated previously required recalibration. We present here results of recalibration efforts using >250 seroconversion panels and multiple statistical methods to ensure accuracy and consensus.
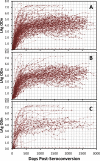
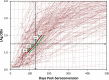
Methods: A total of 2737 longitudinal specimens collected from 259 seroconverting individuals infected with diverse HIV-1 subtypes were tested with the LAg-Avidity EIA as previously described. Data were analyzed for determination of MDRI at ODn cutoffs of 1.0 to 2.0 using 7 statistical approaches and sub-analyzed by HIV-1 subtypes. In addition, 3740 specimens from individuals with infection >1 year, including 488 from patients with AIDS, were tested for PFR at varying cutoffs.
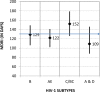
Results: Using different statistical methods, MDRI values ranged from 88-94 days at cutoff ODn = 1.0 to 177-183 days at ODn = 2.0. The MDRI values were similar by different methods suggesting coherence of different approaches. Testing for misclassification among long-term infections indicated that overall PFRs were 0.6% to 2.5% at increasing cutoffs of 1.0 to 2.0, respectively. Balancing the need for a longer MDRI and smaller PFR (<2.0%) suggests that a cutoff ODn = 1.5, corresponding to an MDRI of 130 days should be used for cross-sectional application. The MDRI varied among subtypes from 109 days (subtype A&D) to 152 days (subtype C).
Conclusions: Based on the new data and revised analysis, we recommend an ODn cutoff = 1.5 to classify recent and long-term infections, corresponding to an MDRI of 130 days (118-142). Determination of revised parameters for estimation of HIV-1 incidence should facilitate application of the LAg-Avidity EIA for worldwide use.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Parekh BS, Hu DJ, Vanichseni S, Satten GA, Candal D, et al. (2001) Evaluation of a sensitive/less-sensitive testing algorithm using the 3A11-LS assay for detecting recent HIV seroconversion, among individuals with HIV-1 subtype B or E infection in Thailand. AIDS Research & Human Retroviruses 17: 453–458. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001777 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Parekh BS, Kennedy MS, Dobbs T, Pau CP, Byers R, et al. (2002) Quantitative detection of increasing HIV type 1 antibodies after seroconversion: a simple assay for detecting recent HIV infection and estimating incidence. AIDS Research & Human Retroviruses 18: 295–307. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001777 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Parekh BS, McDougal JS (2005) Application of laboratory methods for estimation of HIV-1 incidence. Indian Journal of Medical Research 121: 510–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

