Retrospective quality control review of FDG scans in the imaging sub-study of PALETTE EORTC 62072/VEG110727: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial
- PMID: 25711176
- PMCID: PMC4382532
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-015-3002-0
Retrospective quality control review of FDG scans in the imaging sub-study of PALETTE EORTC 62072/VEG110727: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial
Abstract
Purpose: (18)F-Labelled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) can detect early changes in tumour metabolism and may be a useful quantitative imaging biomarker (QIB) for prediction of disease stabilization, response and duration of progression-free survival (PFS). Standardization of imaging procedures is a prerequisite, especially in multicentre clinical trials. In this study we reviewed the quality of FDG scans and compliance with the imaging guideline (IG) in a phase III clinical trial.
Methods: Forty-four cancer patients were enroled in an imaging sub-study of a randomized international multicentre trial. FDG scan had to be performed at baseline and 10-14 days after treatment start. The image transmittal forms (ITFs) and Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) [1] standard headers were analysed for compliance with the IG. Mean liver standardized uptake values (LSUVmean) were measured as recommended by positron emission tomography (PET) Response Criteria in Solid Tumors 1.0 (PERCIST) [2].
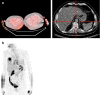
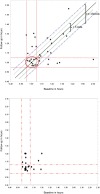
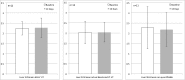
Results: Of 88 scans, 81 were received (44 patients); 36 were properly anonymized; 77/81 serum glucose values submitted, all but one within the IG. In 35/44 patients both scans were of sufficient visual quality. In 22/70 ITFs the reported UT differed by >1 min from the DICOM headers (max. difference 1 h 4 min). Based on the DICOM, UT compliance for both scans was 31.4%. LSUVmean was fairly constant for the 11 patients with UT compliance: 2.30 ± 0.33 at baseline and 2.27 ± 0.48 at follow-up (FU). Variability substantially increased for the subjects with unacceptable UT (11 patients): 2.27 ± 1.04 at baseline and 2.18 ± 0.83 at FU.
Conclusion: The high attrition number of patients due to low compliance with the IG compromised the quantitative assessment of the predictive value for early response monitoring. This emphasizes the need for better regulated procedures in imaging departments, which may be achieved by education of involved personnel or efforts towards regulations. LSUVmean could be monitored to assess quality and compliance in an FDG PET/CT study.
Figures
References
-
- http://dicom.nema.org. Accessed 18 Jul 2014.
-
- Stroobants S, Goeminne J, Seegers M, Dimitrijevic S, Dupont P, Nuyts J, et al. 18FDG-Positron emission tomography for the early prediction of response in advanced soft tissue sarcoma treated with imatinib mesylate (Glivec) Eur J Cancer. 2003;39(14):2012–2020. doi: 10.1016/S0959-8049(03)00073-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zander T, Scheffler M, Nogova L, Kobe C, Engel-Riedel W, Hellmich M, et al. Early prediction of nonprogression in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib by using [(18)F]fluorodeoxyglucose and [(18)F]fluorothymidine positron emission tomography. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(13):1701–1708. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.32.4939. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

