Di-sulfated Keratan Sulfate as a Novel Biomarker for Mucopolysaccharidosis II, IVA, and IVB
- PMID: 25712379
- PMCID: PMC4470954
- DOI: 10.1007/8904_2014_330
Di-sulfated Keratan Sulfate as a Novel Biomarker for Mucopolysaccharidosis II, IVA, and IVB
Abstract
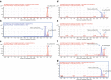
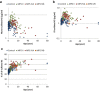
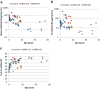
Keratan sulfate (KS) is a storage material in mucopolysaccharidosis IV (MPS IV). However, no detailed analysis has been reported on subclasses of KS: mono-sulfated KS and di-sulfated KS. We established a novel method to distinguish and quantify mono- and di-sulfated KS using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and measured both KS levels in various specimens.Di-sulfated KS was dominant in shark cartilage and rat serum, while mono-sulfated KS was dominant in bovine cornea and human serum. Levels of both mono- and di-sulfated KS varied with age in the blood and urine from control subjects and patients with MPS II and IVA. The mean levels of both forms of KS in the plasma/serum from patients with MPS II, IVA, and IVB were elevated compared with that in age-matched controls. Di-sulfated KS provided more significant difference between MPS IVA and the age-matched controls than mono-sulfated KS. The ratio of di-sulfated KS to total KS in plasma/serum increased with age in control subjects and patients with MPS II but was age independent in MPS IVA patients. Consequently, this ratio can discriminate younger MPS IVA patients from controls. Levels of mono- and di-sulfated KS in urine of MPS IVA and IVB patients were all higher than age-matched controls for all ages studied.In conclusion, the level of di-sulfated KS and its ratio to total KS can distinguish control subjects from patients with MPS II, IVA, and IVB, indicating that di-sulfated KS may be a novel biomarker for these disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Bhavanandan VP, Meyer K. Studies on keratosulfates. Methylation, desulfation, and acid hydrolysis studies on old human rib cartilage keratosulfate. J Biol Chem. 1968;243:1052–1059. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

