Selection and Counterselection of Hia Expression Reveals a Key Role for Phase-Variable Expression of Hia in Infection Caused by Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae
- PMID: 25712964
- PMCID: PMC4539897
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiv103
Selection and Counterselection of Hia Expression Reveals a Key Role for Phase-Variable Expression of Hia in Infection Caused by Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae
Abstract
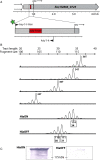
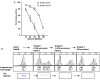
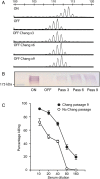
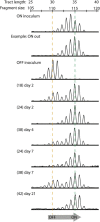
Hia is a major adhesin of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) and has long been investigated as a vaccine candidate. Here we show that Hia phase variation is controlled by changes in the length of a polythymidine tract located in the hia promoter. Studies of an invasive clinical isolate (strain R2866) show that strains expressing high Hia levels are more efficiently killed by opsonophagocytosis. An opsonophagocytic assay was used to select for a subpopulation of variants that expressed a low level of Hia, which facilitated their escape from killing by anti-Hia antisera. Conversely, a subpopulation of variants expressing a high level of Hia was selected for during passaging through Chang cells. In both cases, phase variation of Hia expression corresponded directly with discrete modal changes in polythymidine tract length. In the chinchilla model of NTHi infection, we observed consistent selection for high Hia expression upon nasopharyngeal colonization, confirming the key role of phase-variable expression of Hia within a specific niche in vivo.
Keywords: Haemophilus; adhesion; colonization; phase variation.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Haggard M. Otitis media: prospects for prevention. Vaccine 2008; 26(suppl 7):G20–4. - PubMed
-
- Johnson RH. Community-acquired pneumonia: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Clin Ther 1988; 10:568–73. - PubMed
-
- Sethi S, Murphy TF. Infection in the pathogenesis and course of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 2008; 359:2355–65. - PubMed
-
- A.A.P. Diagnosis and management of acute otitis media. Pediatrics 2004; 113:1451–65. - PubMed
-
- Alsarraf R, Jung CJ, Perkins J, Crowley C, Alsarraf NW, Gates GA. Measuring the indirect and direct costs of acute otitis media. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1999; 125:12–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

