Cyclic AMP signaling reduces sirtuin 6 expression in non-small cell lung cancer cells by promoting ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation via inhibition of the Raf-MEK-ERK (Raf/mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase) pathway
- PMID: 25713071
- PMCID: PMC4392263
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.633198
Cyclic AMP signaling reduces sirtuin 6 expression in non-small cell lung cancer cells by promoting ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation via inhibition of the Raf-MEK-ERK (Raf/mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase) pathway
Abstract
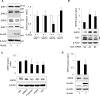
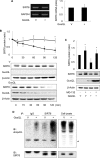
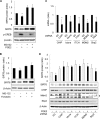
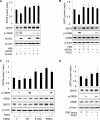
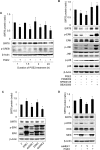
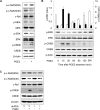
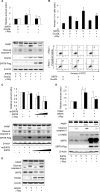
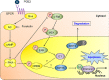
The cAMP signaling system regulates various cellular functions, including metabolism, gene expression, and death. Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) removes acetyl groups from histones and regulates genomic stability and cell viability. We hypothesized that cAMP modulates SIRT6 activity to regulate apoptosis. Therefore, we examined the effects of cAMP signaling on SIRT6 expression and radiation-induced apoptosis in lung cancer cells. cAMP signaling in H1299 and A549 human non-small cell lung cancer cells was activated via the expression of constitutively active Gαs plus treatment with prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), isoproterenol, or forskolin. The expression of sirtuins and signaling molecules were analyzed by Western blotting. Activation of cAMP signaling reduced SIRT6 protein expression in lung cancer cells. cAMP signaling increased the ubiquitination of SIRT6 protein and promoted its degradation. Treatment with MG132 and inhibiting PKA with H89 or with a dominant-negative PKA abolished the cAMP-mediated reduction in SIRT6 levels. Treatment with PGE2 inhibited c-Raf activation by increasing inhibitory phosphorylation at Ser-259 in a PKA-dependent manner, thereby inhibiting downstream MEK-ERK signaling. Inhibiting ERK with inhibitors or with dominant-negative ERKs reduced SIRT6 expression, whereas activation of ERK by constitutively active MEK abolished the SIRT6-depleting effects of PGE2. cAMP signaling also augmented radiation-induced apoptosis in lung cancer cells. This effect was abolished by exogenous expression of SIRT6. It is concluded that cAMP signaling reduces SIRT6 expression by promoting its ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent degradation, a process mediated by the PKA-dependent inhibition of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway. Reduced SIRT6 expression mediates the augmentation of radiation-induced apoptosis by cAMP signaling in lung cancer cells.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cyclic AMP (cAMP); Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase (ERK); Lung Cancer; Protein Kinase A (PKA); Sirtuin.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effect of PGE2 on EGF-induced MAP kinase activity and rabbit corneal epithelial proliferation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000 Jul;41(8):2164-9. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000. PMID: 10892858
-
Exchange proteins directly activated by cAMP induce the proliferation of rat anterior pituitary GH3 cells via the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Apr 1;485(2):355-359. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.075. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28216156
-
cAMP inhibits the proliferation of retinal pigmented epithelial cells through the inhibition of ERK1/2 in a PKA-independent manner.Oncogene. 2002 Sep 5;21(39):6101-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205765. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12203122
-
Extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK)-independent functions of Raf kinases.J Cell Sci. 2002 Apr 15;115(Pt 8):1575-81. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.8.1575. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 11950876 Review.
-
Signaling threshold regulation by the Ras effector IMP.J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 24;284(17):11007-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800082200. Epub 2008 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19091743 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of HOXA13 as a potential tumorigenesis and progression promoter of LUSC based on qRT-PCR and bioinformatics.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Oct 1;10(10):10650-10665. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966409 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic interface between ubiquitylation and cAMP signaling.Front Pharmacol. 2015 Sep 4;6:177. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00177. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26388770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MEK1 signaling promotes self-renewal and tumorigenicity of liver cancer stem cells via maintaining SIRT1 protein stabilization.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 12;7(15):20597-611. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7972. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26967560 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Cancer Cell Responsiveness to Ionizing Radiation Treatment by Cyclic AMP Response Element Binding Nuclear Transcription Factor.Front Oncol. 2017 May 5;7:76. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00076. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28529924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin-dependent clock control: new advances in metabolism, aging and cancer.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015 Nov;18(6):521-7. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000219. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015. PMID: 26335311 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A., Bray F., Center M. M., Ferlay J., Ward E., Forman D. (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 61, 69–90 - PubMed
-
- Zochbauer-Muller S., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. (2002) Molecular pathogenesis of lung cancer. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64, 681–708 - PubMed
-
- Govindan R., Page N., Morgensztern D., Read W., Tierney R., Vlahiotis A., Spitznagel E. L., Piccirillo J. (2006) Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 4539–4544 - PubMed
-
- Johnson D. H., Schiller J. H., Bunn P. A., Jr. (2014) Recent clinical advances in lung cancer management. J. Clin. Oncol. 32, 973–982 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

