A metal-containing nucleoside that possesses both therapeutic and diagnostic activity against cancer
- PMID: 25713072
- PMCID: PMC4392271
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.620294
A metal-containing nucleoside that possesses both therapeutic and diagnostic activity against cancer
Abstract
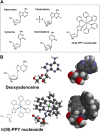
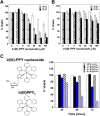
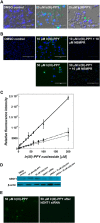
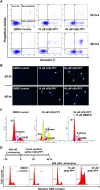
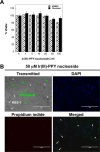
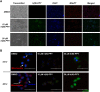
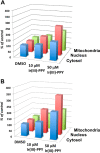
Nucleoside transport is an essential process that helps maintain the hyperproliferative state of most cancer cells. As such, it represents an important target for developing diagnostic and therapeutic agents that can effectively detect and treat cancer, respectively. This report describes the development of a metal-containing nucleoside designated Ir(III)-PPY nucleoside that displays both therapeutic and diagnostic properties against the human epidermal carcinoma cell line KB3-1. The cytotoxic effects of Ir(III)-PPY nucleoside are both time- and dose-dependent. Flow cytometry analyses validate that the nucleoside analog causes apoptosis by blocking cell cycle progression at G2/M. Fluorescent microscopy studies show rapid accumulation in the cytoplasm within 4 h. However, more significant accumulation is observed in the nucleus and mitochondria after 24 h. This localization is consistent with the ability of the metal-containing nucleoside to influence cell cycle progression at G2/M. Mitochondrial depletion is also observed after longer incubations (Δt ∼48 h), and this effect may produce additional cytotoxic effects. siRNA knockdown experiments demonstrate that the nucleoside transporter, hENT1, plays a key role in the cellular entry of Ir(III)-PPY nucleoside. Collectively, these data provide evidence for the development of a metal-containing nucleoside that functions as a combined therapeutic and diagnostic agent against cancer.
Keywords: Cancer Therapy; Molecular Imaging; Molecular Pharmacology; Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analogue; Transport.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycine 154 of the equilibrative nucleoside transporter, hENT1, is important for nucleoside transport and for conferring sensitivity to the inhibitors nitrobenzylthioinosine, dipyridamole, and dilazep.Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Feb 1;67(3):453-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2003.09.018. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15037197
-
Downregulation of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 by RNAi enhances 5-fluorouracil response in pancreatic cancer.Hepatogastroenterology. 2010 Nov-Dec;57(104):1567-72. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 21443122
-
Cytotoxic activities of nucleoside and nucleobase analog drugs in malignant mesothelioma: characterization of a novel nucleobase transport activity.Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 May 15;75(10):1901-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.02.006. Epub 2008 Feb 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18371936
-
The induction of apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells through the ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction pathway by a Ir(III) complex.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2016 Dec;21(8):1047-1060. doi: 10.1007/s00775-016-1401-8. Epub 2016 Oct 28. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2016. PMID: 27796592
-
Human equilibrative nucleoside transporter (ENT) family of nucleoside and nucleobase transporter proteins.Xenobiotica. 2008 Jul;38(7-8):995-1021. doi: 10.1080/00498250801927427. Xenobiotica. 2008. PMID: 18668437 Review.
Cited by
-
Shining New Light on Biological Systems: Luminescent Transition Metal Complexes for Bioimaging and Biosensing Applications.Chem Rev. 2024 Aug 14;124(15):8825-9014. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00629. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39052606 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tiwari K. N., Cappellacci L., Montgomery J. A., Secrist J. A., 3rd (2003) Synthesis and anti-cancer activity of some novel 5-azacytosine nucleosides. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 22, 2161–2170 - PubMed
-
- Wang M., Liu Y., Liu S., Zheng D. (2004) 8-Chloro-adenosine sensitizes a human hepatoma cell line to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by caspase-dependent and -independent pathways. Oncol. Rep. 12, 193–199 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

