Transcriptional activity of the islet β cell factor Pdx1 is augmented by lysine methylation catalyzed by the methyltransferase Set7/9
- PMID: 25713082
- PMCID: PMC4392279
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.616219
Transcriptional activity of the islet β cell factor Pdx1 is augmented by lysine methylation catalyzed by the methyltransferase Set7/9
Abstract
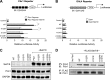
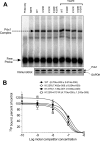
The transcription factor Pdx1 is crucial to islet β cell function and regulates target genes in part through interaction with coregulatory factors. Set7/9 is a Lys methyltransferase that interacts with Pdx1. Here we tested the hypothesis that Lys methylation of Pdx1 by Set7/9 augments Pdx1 transcriptional activity. Using mass spectrometry and mutational analysis of purified proteins, we found that Set7/9 methylates the N-terminal residues Lys-123 and Lys-131 of Pdx1. Methylation of these residues occurred only in the context of intact, full-length Pdx1, suggesting a specific requirement of secondary and/or tertiary structural elements for catalysis by Set7/9. Immunoprecipitation assays and mass spectrometric analysis using β cells verified Lys methylation of endogenous Pdx1. Cell-based luciferase reporter assays using wild-type and mutant transgenes revealed a requirement of Pdx1 residue Lys-131, but not Lys-123, for transcriptional augmentation by Set7/9. Lys-131 was not required for high-affinity interactions with DNA in vitro, suggesting that its methylation likely enhances post-DNA binding events. To define the role of Set7/9 in β cell function, we generated mutant mice in which the gene encoding Set7/9 was conditionally deleted in β cells (Set(Δ)β). Set(Δ)β mice exhibited glucose intolerance similar to Pdx1-deficient mice, and their isolated islets showed impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion with reductions in expression of Pdx1 target genes. Our results suggest a previously unappreciated role for Set7/9-mediated methylation in the maintenance of Pdx1 activity and β cell function.
Keywords: Diabetes; Gene Knockout; Pdx1; Protein Methylation; Set7/9; Transcription; pancreatic Islet.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Ferrannini E., Gastaldelli A., Miyazaki Y., Matsuda M., Mari A., DeFronzo R. A. (2005) β-Cell function in subjects spanning the range from normal glucose tolerance to overt diabetes: a new analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90, 493–500 - PubMed
-
- Jonsson J., Carlsson L., Edlund T., Edlund H. (1994) Insulin-promoter-factor 1 is required for pancreas development in mice. Nature 371, 606–609 - PubMed
-
- Offield M. F., Jetton T. L., Labosky P. A., Ray M., Stein R. W., Magnuson M. A., Hogan B. L., Wright C. V. (1996) PDX-1 is required for pancreatic outgrowth and differentiation of the rostral duodenum. Development 122, 983–995 - PubMed
-
- Stoffers D. A., Zinkin N. T., Stanojevic V., Clarke W. L., Habener J. F. (1997) Pancreatic agenesis attributable to a single nucleotide deletion in the human IPF1 gene coding sequence. Nat. Genet. 15, 106–110 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

