Recruitment of the adaptor protein Nck to PECAM-1 couples oxidative stress to canonical NF-κB signaling and inflammation
- PMID: 25714462
- PMCID: PMC4413941
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2005648
Recruitment of the adaptor protein Nck to PECAM-1 couples oxidative stress to canonical NF-κB signaling and inflammation
Abstract
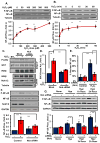
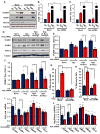
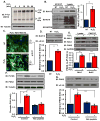
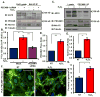
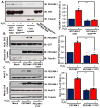
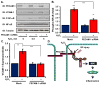
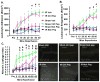
Oxidative stress stimulates nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation and NF-κB-dependent proinflammatory gene expression in endothelial cells during several pathological conditions, including ischemia/reperfusion injury. We found that the Nck family of adaptor proteins linked tyrosine kinase signaling to oxidative stress-induced activation of NF-κB through the classic IκB kinase-dependent pathway. Depletion of Nck prevented oxidative stress induced by exogenous hydrogen peroxide or hypoxia/reoxygenation injury from activating NF-κB in endothelial cells, increasing the abundance of the proinflammatory molecules ICAM-1 (intracellular adhesion molecule-1) and VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule-1) and recruiting leukocytes. Nck depletion also attenuated endothelial cell expression of genes encoding proinflammatory factors but not those encoding antioxidants. Nck promoted oxidative stress-induced activation of NF-κB by coupling the tyrosine phosphorylation of PECAM-1 (platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1) to the activation of p21-activated kinase, which mediates oxidative stress-induced NF-κB signaling. Consistent with this mechanism, treatment of mice subjected to ischemia/reperfusion injury in the cremaster muscle with a Nck inhibitory peptide blocked leukocyte adhesion and emigration and the accompanying vascular leak. Together, these data identify Nck as an important mediator of oxidative stress-induced inflammation and a potential therapeutic target for ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chitosan oligosaccharides prevented retinal ischemia and reperfusion injury via reduced oxidative stress and inflammation in rats.Exp Eye Res. 2015 Jan;130:38-50. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.12.001. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Exp Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 25479043
-
PM2.5-induced oxidative stress increases adhesion molecules expression in human endothelial cells through the ERK/AKT/NF-κB-dependent pathway.J Appl Toxicol. 2016 Jan;36(1):48-59. doi: 10.1002/jat.3143. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Appl Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 25876056
-
Classical NF-κB activation impairs skeletal muscle oxidative phenotype by reducing IKK-α expression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1842(2):175-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24215713
-
Modulation of neuro-inflammation and vascular response by oxidative stress following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(1):1-14. doi: 10.2174/092986708783330665. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18220759 Review.
-
Anoxia/reoxygenation-induced leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions.Free Radic Biol Med. 2002 Aug 15;33(4):427-32. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(02)00852-3. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002. PMID: 12160924 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma proteome association with coronary heart disease and carotid intima media thickness: results from the KORA F4 study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 May 29;23(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02274-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38811951 Free PMC article.
-
Nck1, But Not Nck2, Mediates Disturbed Flow-Induced p21-Activated Kinase Activation and Endothelial Permeability.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jun 2;9(11):e016099. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016099. Epub 2020 May 29. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32468886 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating PAK1: Accessory Proteins as Promising Therapeutic Targets.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 7;15(2):242. doi: 10.3390/biom15020242. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide-based sequestration of the adaptor protein Nck1 in pancreatic β cells enhances insulin biogenesis and protects against diabetogenic stresses.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 10;293(32):12516-12524. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002728. Epub 2018 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29941454 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial NCK2 promotes atherosclerosis progression in male but not female Nck1-null atheroprone mice.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 12;9:955027. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.955027. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36035930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Ghouleh I, Khoo NK, Knaus UG, Griendling KK, Touyz RM, Thannickal VJ, Barchowsky A, Nauseef WM, Kelley EE, Bauer PM, Darley-Usmar V, Shiva S, Cifuentes-Pagano E, Freeman BA, Gladwin MT, Pagano PJ. Oxidases and peroxidases in cardiovascular and lung disease: new concepts in reactive oxygen species signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;51:1271–1288. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gloire G, Legrand-Poels S, Piette J. NF-kappaB activation by reactive oxygen species: fifteen years later. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72:1493–1505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

