The emerging role of lysine demethylases in DNA damage response: dissecting the recruitment mode of KDM4D/JMJD2D to DNA damage sites
- PMID: 25714495
- PMCID: PMC4614868
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1014147
The emerging role of lysine demethylases in DNA damage response: dissecting the recruitment mode of KDM4D/JMJD2D to DNA damage sites
Abstract
KDM4D is a lysine demethylase that removes tri- and di- methylated residues from H3K9 and is involved in transcriptional regulation and carcinogenesis. We recently showed that KDM4D is recruited to DNA damage sites in a PARP1-dependent manner and facilitates double-strand break repair in human cells. Moreover, we demonstrated that KDM4D is an RNA binding protein and mapped its RNA-binding motifs. Interestingly, KDM4D-RNA interaction is essential for its localization on chromatin and subsequently for efficient demethylation of its histone substrate H3K9me3. Here, we provide new data that shed mechanistic insights into KDM4D accumulation at DNA damage sites. We show for the first time that KDM4D binds poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) in vitro via its C-terminal region. In addition, we demonstrate that KDM4D-RNA interaction is required for KDM4D accumulation at DNA breakage sites. Finally, we discuss the recruitment mode and the biological functions of additional lysine demethylases including KDM4B, KDM5B, JMJD1C, and LSD1 in DNA damage response.
Keywords: DNA damage response (DDR); KDM4D; PARP1; and cancer; chromosomal instability; double strand break (DSB); lysine demethylases (KDM); poly(ADP-ribose)ylation (PARylation).
Figures

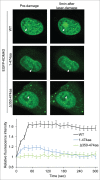
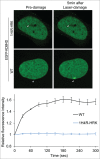
Comment in
-
KDM4D crosstalks with PARP1 and RNA at DNA DSBs.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(10):1495. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1032648. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25835072 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
PARP1-dependent recruitment of KDM4D histone demethylase to DNA damage sites promotes double-strand break repair.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Feb 18;111(7):E728-37. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1317585111. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24550317 Free PMC article.
-
Kdm4b histone demethylase is a DNA damage response protein and confers a survival advantage following γ-irradiation.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 19;288(29):21376-21388. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.491514. Epub 2013 Jun 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23744078 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-dependent chromatin localization of KDM4D lysine demethylase promotes H3K9me3 demethylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Dec 1;42(21):13026-38. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1021. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25378304 Free PMC article.
-
Joining the PARty: PARP Regulation of KDM5A during DNA Repair (and Transcription?).Bioessays. 2022 Jul;44(7):e2200015. doi: 10.1002/bies.202200015. Epub 2022 May 9. Bioessays. 2022. PMID: 35532219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KDM4/JMJD2 histone demethylases: epigenetic regulators in cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2013 May 15;73(10):2936-42. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4300. Epub 2013 May 3. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23644528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deubiquitinase USP7 stabilizes KDM5B and promotes tumor progression and cisplatin resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the ZBTB16/TOP2A axis.Cell Death Differ. 2024 Mar;31(3):309-321. doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01257-x. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Cell Death Differ. 2024. PMID: 38287116 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of the network of histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation in acute myeloid leukaemia.Oncol Rep. 2020 Aug;44(2):543-554. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7627. Epub 2020 May 28. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32468066 Free PMC article.
-
T Cells Spatially Regulate B Cell Receptor Signaling in Lymphomas through H3K9me3 Modifications.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Feb;14(5):e2401192. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202401192. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 38837879 Free PMC article.
-
Role of H3K9 demethylases in DNA double-strand break repair.J Cancer Biol. 2020;1(1):10-15. doi: 10.46439/cancerbiology.1.003. J Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 32696030 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of Jumonji C domain-containing histone lysine demethylases overcome cisplatin and paclitaxel resistance in non-small cell lung cancer through APC/Cdh1-dependent degradation of CtIP and PAF15.Cancer Biol Ther. 2022 Dec 31;23(1):65-75. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2021.2020060. Cancer Biol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35100078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindahl T. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature 1993; 362:709-15; PMID:8469282; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/362709a0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lindahl T, Barnes DE. Repair of endogenous DNA damage. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 2000; 65:127-33; PMID:12760027; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/sqb.2000.65.127 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jackson SP, Bartek J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009; 461:1071-8; PMID:19847258; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature08467 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lord CJ, Ashworth A. The DNA damage response and cancer therapy. Nature 2012; 481:287-94; PMID:22258607; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature10760 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cassidy LD, Liau SS, Venkitaraman AR. Chromosome instability and carcinogenesis: insights from murine models of human pancreatic cancer associated with BRCA2 inactivation. Mol Oncol 2014; 8:161-8; PMID:24268522; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2013.10.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
