Genetics of wellbeing and its components satisfaction with life, happiness, and quality of life: a review and meta-analysis of heritability studies
- PMID: 25715755
- PMCID: PMC4346667
- DOI: 10.1007/s10519-015-9713-y
Genetics of wellbeing and its components satisfaction with life, happiness, and quality of life: a review and meta-analysis of heritability studies
Abstract
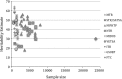
Wellbeing is a major topic of research across several disciplines, reflecting the increasing recognition of its strong value across major domains in life. Previous twin-family studies have revealed that individual differences in wellbeing are accounted for by both genetic as well as environmental factors. A systematic literature search identified 30 twin-family studies on wellbeing or a related measure such as satisfaction with life or happiness. Review of these studies showed considerable variation in heritability estimates (ranging from 0 to 64 %), which makes it difficult to draw firm conclusions regarding the genetic influences on wellbeing. For overall wellbeing twelve heritability estimates, from 10 independent studies, were meta-analyzed by computing a sample size weighted average heritability. Ten heritability estimates, derived from 9 independent samples, were used for the meta-analysis of satisfaction with life. The weighted average heritability of wellbeing, based on a sample size of 55,974 individuals, was 36 % (34-38), while the weighted average heritability for satisfaction with life was 32 % (29-35) (n = 47,750). With this result a more robust estimate of the relative influence of genetic effects on wellbeing is provided.
Figures

References
-
- Allardt E (1973) About dimension of welfare: an exploratory analysis of the comparative Scandinavian survey. In: Reports RGoCSR (ed). University of Helsinki
-
- Andrews FM, McKennell AC. Measures of self-reported well-being: their affective, cognitive, and other components. Soc Indicator Res. 1980;8:127–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00286474. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

