Hippocampal Wnt Signaling: Memory Regulation and Hormone Interactions
- PMID: 25717070
- PMCID: PMC7053425
- DOI: 10.1177/1073858415574728
Hippocampal Wnt Signaling: Memory Regulation and Hormone Interactions
Abstract
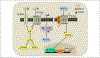
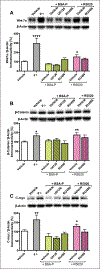
Wnt signaling has emerged in recent years as a major player in both nervous system development and adult synaptic plasticity. Of particular relevance to researchers studying learning and memory, Wnt signaling is critical for normal functioning of the hippocampus, a brain region that is essential for many types of memory formation and whose dysfunction is implicated in numerous neurodegenerative and psychiatric conditions. Impaired hippocampal Wnt signaling is implicated in several of these conditions, however, little is known about how Wnt signaling mediates hippocampal memory formation. This review will provide a general overview of Wnt signaling and discuss evidence demonstrating a key role for Wnt signaling in hippocampal memory formation in both normal and disease states. The regulation of Wnt signaling by ovarian sex steroid hormones will also be highlighted, given that the neuroprotection afforded by Wnt-hormone interactions may have significant implications for cognitive function in aging, neurodegenerative disease, and ischemic injury.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; GSK3β; estradiol; hippocampus; progesterone; β-catenin.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TGF-β1 Restores Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity and Memory in Alzheimer Model via the PI3K/Akt/Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.J Mol Neurosci. 2019 Jan;67(1):142-149. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1219-7. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30539409
-
Role of Wnt signaling in synaptic plasticity and memory.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2022 Jan;187:107558. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2021.107558. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2022. PMID: 34808336 Review.
-
Aberrant Wnt signaling pathway in medial temporal lobe structures of Alzheimer's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015 Sep;122(9):1303-18. doi: 10.1007/s00702-015-1375-7. Epub 2015 Feb 14. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015. PMID: 25680440
-
Wnt signaling in the nervous system and in Alzheimer's disease.J Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;6(1):64-74. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjt051. J Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24549157 Review.
-
Resveratrol Mediated Regulation of Hippocampal Neuroregenerative Plasticity via SIRT1 Pathway in Synergy with Wnt Signaling: Neurotherapeutic Implications to Mitigate Memory Loss in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;94(s1):S125-S140. doi: 10.3233/JAD-220559. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 36463442 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered DNA Methylation Patterns Associated With Clinically Relevant Increases in PTSD Symptoms and PTSD Symptom Profiles in Military Personnel.Biol Res Nurs. 2018 May;20(3):352-358. doi: 10.1177/1099800418758951. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Biol Res Nurs. 2018. PMID: 29514460 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Acyclovir and IVIG on Behavioral Outcomes after HSV1 CNS Infection.Behav Neurol. 2017;2017:5238402. doi: 10.1155/2017/5238402. Epub 2017 Nov 19. Behav Neurol. 2017. PMID: 29358844 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the potential anti-senescence effects of soybean-derived peptide Soymetide in mice hippocampal neurons via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 25;16:1510337. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1510337. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40070562 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral changes and gene profile alterations after chronic 1,950-MHz radiofrequency exposure: An observation in C57BL/6 mice.Brain Behav. 2020 Nov;10(11):e01815. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1815. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Brain Behav. 2020. PMID: 32856797 Free PMC article.
-
Frizzled 1 and Wnt1 as new potential therapeutic targets in the traumatically injured spinal cord.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Nov;77(22):4631-4662. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03427-4. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31900623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez AR, Godoy JA, Mullendorff K, Olivares GH, Bronfman M, Inestrosa NC. 2004. Wnt-3a overcomes beta-amyloid toxicity in rat hippocampal neurons. Exp Cell Res 297:186–96. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2011. 2011 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Washington, DC: Alzheimer’s Association; p 31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

