Oral rivaroxaban for Japanese patients with symptomatic venous thromboembolism - the J-EINSTEIN DVT and PE program
- PMID: 25717286
- PMCID: PMC4339301
- DOI: 10.1186/s12959-015-0035-3
Oral rivaroxaban for Japanese patients with symptomatic venous thromboembolism - the J-EINSTEIN DVT and PE program
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: 'Oral rivaroxaban for Japanese patients with symptomatic venous thromboembolism - the J-EINSTEIN DVT and PE program'.Thromb J. 2016 May 23;14:11. doi: 10.1186/s12959-016-0085-1. eCollection 2016. Thromb J. 2016. PMID: 27222638 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The global EINSTEIN DVT and PE studies compared rivaroxaban (15 mg twice daily for 3 weeks followed by 20 mg once daily) with enoxaparin/vitamin K antagonist therapy and demonstrated non-inferiority for efficacy and superiority for major bleeding. Owing to differences in targeted anticoagulant intensities in Japan, Japanese patients were not enrolled into the global studies. Instead, a separate study of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) in Japanese patients was conducted, which compared the Japanese standard of care with a reduced dose of rivaroxaban.
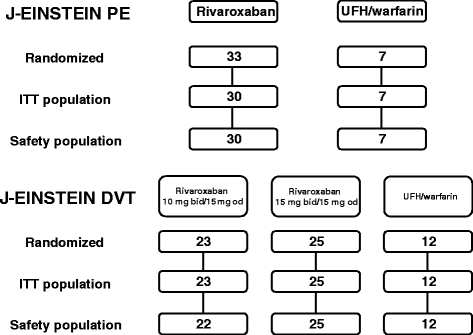
Methods: We conducted an open-label, randomized trial that compared 3, 6, or 12 months of oral rivaroxaban alone (10 mg twice daily or 15 mg twice daily for 3 weeks followed by 15 mg once daily) with activated partial thromboplastin time-adjusted intravenous unfractionated heparin (UFH) followed by warfarin (target international normalized ratio 2.0; range 1.5-2.5) in patients with acute, objectively confirmed symptomatic DVT and/or PE. Patients were assessed for the occurrence of symptomatic recurrent venous thromboembolic events or asymptomatic deterioration and bleeding.
Results: Eighty-one patients were assigned to rivaroxaban and 19 patients to UFH/warfarin. Three patients were excluded because of serious non-compliance issues. The composite of symptomatic venous thromboembolic events or asymptomatic deterioration occurred in 1 (1.4%) rivaroxaban patient and in 1 (5.3%) UFH/warfarin patient (absolute risk difference, 3.9% [95% confidence interval, -3.4-23.8]). No major bleeding occurred during study treatment. Clinically relevant non-major bleeding occurred in 6 (7.8%) patients in the rivaroxaban group and 1 (5.3%) patient in the UFH/warfarin group.
Conclusions: The findings of this study in Japanese patients with acute DVT and/or PE suggest a similar efficacy and safety profile with rivaroxaban and control treatment, consistent with that of the worldwide EINSTEIN DVT and PE program.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT01516840 and NCT01516814.
Keywords: Deep vein thrombosis; Japan; Pulmonary embolism; Randomized trial; Rivaroxaban; Unfractionated heparin; Venous thromboembolism; Warfarin.
Figures
References
-
- Oger E. Incidence of venous thromboembolism: a community-based study in Western France. EPI-GETBP study group. Groupe d’Etude de la Thrombose de Bretagne Occidentale. Thromb Haemost. 2000;83:657–60. - PubMed
-
- Cohen AT, Agnelli G, Anderson FA, Arcelus JI, Bergqvist D, Brecht JG, et al. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) in Europe. The number of VTE events and associated morbidity and mortality. Thromb Haemost. 2007;98:756–64. - PubMed
-
- Kearon C, Akl EA, Comerota AJ, Prandoni P, Bounameaux H, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012;141:e419S–94. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-2301. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical