Family-based programmes for preventing smoking by children and adolescents
- PMID: 25720328
- PMCID: PMC6486099
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004493.pub3
Family-based programmes for preventing smoking by children and adolescents
Abstract
Background: There is evidence that family and friends influence children's decisions to smoke.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness of interventions to help families stop children starting smoking.
Search methods: We searched 14 electronic bibliographic databases, including the Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Group specialized register, MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, CINAHL unpublished material, and key articles' reference lists. We performed free-text internet searches and targeted searches of appropriate websites, and hand-searched key journals not available electronically. We consulted authors and experts in the field. The most recent search was 3 April 2014. There were no date or language limitations.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of interventions with children (aged 5-12) or adolescents (aged 13-18) and families to deter tobacco use. The primary outcome was the effect of the intervention on the smoking status of children who reported no use of tobacco at baseline. Included trials had to report outcomes measured at least six months from the start of the intervention.
Data collection and analysis: We reviewed all potentially relevant citations and retrieved the full text to determine whether the study was an RCT and matched our inclusion criteria. Two authors independently extracted study data for each RCT and assessed them for risk of bias. We pooled risk ratios using a Mantel-Haenszel fixed effect model.
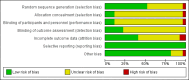
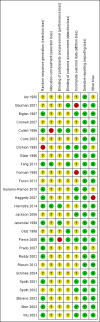
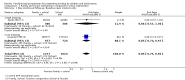
Main results: Twenty-seven RCTs were included. The interventions were very heterogeneous in the components of the family intervention, the other risk behaviours targeted alongside tobacco, the age of children at baseline and the length of follow-up. Two interventions were tested by two RCTs, one was tested by three RCTs and the remaining 20 distinct interventions were tested only by one RCT. Twenty-three interventions were tested in the USA, two in Europe, one in Australia and one in India.The control conditions fell into two main groups: no intervention or usual care; or school-based interventions provided to all participants. These two groups of studies were considered separately.Most studies had a judgement of 'unclear' for at least one risk of bias criteria, so the quality of evidence was downgraded to moderate. Although there was heterogeneity between studies there was little evidence of statistical heterogeneity in the results. We were unable to extract data from all studies in a format that allowed inclusion in a meta-analysis.There was moderate quality evidence family-based interventions had a positive impact on preventing smoking when compared to a no intervention control. Nine studies (4810 participants) reporting smoking uptake amongst baseline non-smokers could be pooled, but eight studies with about 5000 participants could not be pooled because of insufficient data. The pooled estimate detected a significant reduction in smoking behaviour in the intervention arms (risk ratio [RR] 0.76, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.68 to 0.84). Most of these studies used intensive interventions. Estimates for the medium and low intensity subgroups were similar but confidence intervals were wide. Two studies in which some of the 4487 participants already had smoking experience at baseline did not detect evidence of effect (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.93 to 1.17).Eight RCTs compared a combined family plus school intervention to a school intervention only. Of the three studies with data, two RCTS with outcomes for 2301 baseline never smokers detected evidence of an effect (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.75 to 0.96) and one study with data for 1096 participants not restricted to never users at baseline also detected a benefit (RR 0.60, 95% CI 0.38 to 0.94). The other five studies with about 18,500 participants did not report data in a format allowing meta-analysis. One RCT also compared a family intervention to a school 'good behaviour' intervention and did not detect a difference between the two types of programme (RR 1.05, 95% CI 0.80 to 1.38, n = 388).No studies identified any adverse effects of intervention.
Authors' conclusions: There is moderate quality evidence to suggest that family-based interventions can have a positive effect on preventing children and adolescents from starting to smoke. There were more studies of high intensity programmes compared to a control group receiving no intervention, than there were for other compairsons. The evidence is therefore strongest for high intensity programmes used independently of school interventions. Programmes typically addressed family functioning, and were introduced when children were between 11 and 14 years old. Based on this moderate quality evidence a family intervention might reduce uptake or experimentation with smoking by between 16 and 32%. However, these findings should be interpreted cautiously because effect estimates could not include data from all studies. Our interpretation is that the common feature of the effective high intensity interventions was encouraging authoritative parenting (which is usually defined as showing strong interest in and care for the adolescent, often with rule setting). This is different from authoritarian parenting (do as I say) or neglectful or unsupervised parenting.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare
Figures




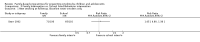
Update of
-
Family-based programmes for preventing smoking by children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD004493. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004493.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 27;(2):CD004493. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004493.pub3. PMID: 17253511 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Ary 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ary DV, Biglan A, Glasgow E, Zoref L. The efficacy of social‐influence prevention programs versus "standard care": Are new initiatives needed?. Journal of Behavioral Medicine 1990;13:281‐96. - PubMed
Bauman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bauman KE, Ennett ST, Foshee VA, Pemberton M, King TS, Koch GG. Influence of a family program on adolescent smoking and drinking prevalence. Prevention Science 2002;3(1):35‐42. - PubMed
-
- Bauman KE, Ennett ST, Foshee VA, Pemberton M, King TS, Koch GG. Influence of a family‐directed program on adolescent cigarette and alcohol cessation. Prevention Science 2000;1(4):227‐37. - PubMed
-
- Ennett ST, Bauman KE, Pemberton M, Foshee VA, Chuang Y‐C, King TS, et al. Mediation in a family‐directed program for prevention of adolescent tobacco and alcohol use. Preventive Medicine 2001;33:333‐46. - PubMed
Biglan 1987 {published data only}
-
- Biglan A, Glasgow RE, Ary DV, Thompson R, Severson H, Lichtenstein E, et al. How generalizable are the effects of smoking prevention programs? Refusal skills training and parent messages in a teacher‐administered program. Journal of Behavioral Medicine 1987;10(6):613‐28. - PubMed
Connell 2007 {published data only}
-
- Connell AM, Dishion TJ, Yasui M, Kavanagh K. An adaptive approach to intervention: Linking engagement in family‐centered intervention to reductions in adolescent problem behavior. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2007;75(4):568‐79. - PubMed
Cullen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Cullen KJ, Cullen AM. Long‐term follow‐up of the Busselton six‐year controlled trial of prevention of children's behavior disorders. Journal of Pediatrics 1996;129:136‐9. - PubMed
Curry 2003 {published data only}
-
- Curry SJ, Hollis J, Bush T, Polen M, Ludman EJ, Grothaus L, et al. A randomized trial of a family‐based smoking prevention intervention in managed care. Preventive Medicine 2003;37(6):617‐26. - PubMed
Dishion 1995 {published data only}
-
- Dishion TJ, Andrews DW. Preventing escalation in problem behaviors with high‐risk young adolescents: immediate and 1‐year outcomes. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1995;63(4):538‐48. - PubMed
-
- Poulin F, Dishion TJ, Kavanagh, Kiesner J. The prevention of behaviour problems in adolescence: the Adolescence Transition Program [La prévention des problèmes de comportement à l'adolescence: Le Adolescent Transition Program]. Criminologie 1998;31(1):67‐85.
Elder 1996 {published data only}
-
- Elder JP, Perry CL, Stone EJ, Johnson CC, Yang M, Edmundson EW, et al. Tobacco use measurement, prediction, and intervention in elementary schools in four states: The CATCH study. Preventive Medicine 1996;25:486‐94. - PubMed
-
- Johnson CC, Osganian SK, Budman SB, Lytle LA, Barrera EP, Bonura SR, et al. CATCH: family process evaluation in a multicenter trial. Health Education Quarterly 1994;Suppl 2:S91‐106. - PubMed
-
- Perry CL, Parcel GS, Stone E, Nader PR, McKinlay SM, Luepker RV, et al. The Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health (CATCH): Overview of the intervention program and evaluation methods. Cardiovascular Risk Factors 1992;2(1):36‐44.
Fang 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fang L, Schinke SP. Alcohol use among Asian American adolescent girls: The impact of psychological and family factors. Journal of Ethnicity in Substance Abuse 2011;10:275‐294. - PubMed
Forman 1990 {published data only}
-
- Forman SG, Linney JA, Brondino MJ. Effects of coping skills training on adolescents at risk for substance use. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 1990;4(2):67‐76.
Fosco 2013 {published and unpublished data}
Guilamo‐Ramos 2010 {published data only}
-
- Guilamo‐Ramos V, Jaccard J, Dittus P, Gonzalez B, Bouris A, Banspach S. The Linking Lives health education program: a randomized clinical trial of a parent‐based tobacco use prevention program for African American and Latino youths. American Journal of Public Health 2010;100(9):1641‐47. - PMC - PubMed
Haggerty 2007 {published data only}
-
- Haggerty KP, Skinner ML, MacKenzie EP, Catalano RF. A randomized trial of Parents Who Care: Effects on key outcomes at 24‐month follow‐up. Prevention Science 2007;8:249‐60. - PubMed
Hiemstra 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hiemstra M, Otten R, Schayck OCP, Engels RCME. Smoking‐specific communication and children's smoking onset: An extension of the theory of planned behavior. Psychology & Health 2013;27(9):1100‐1117. - PubMed
-
- Hiemstra M, Ringlever L, Otten R, Schayck OCP, Engels RCME. Short‐term effects of a home‐based smoking prevention program on antismoking socialization and smoking‐related cognitions: A cluster randomized controlled trial.. European Addiction Research 2013;19:128‐140. - PubMed
-
- Hiemstra M, Ringlever L, Otten R, Schayck OCP, Jackson C, Engels RCME. Long‐term effects of a home‐based smoking prevention program on smoking initiation: A cluster randomized controlled trial. Preventive Medicine 2014;60:65‐70. - PubMed
Jackson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Jackson C, Dickinson D. Enabling parents who smoke to prevent their children from initiating smoking. Results from a 3‐year intervention evaluation. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine 2006;160:56‐62. - PubMed
Jøsendal 1998 {published data only}
-
- Jøsendal O, Aarø LE, Bergh I. Effects of a school‐based smoking prevention program among subgroups of adolescents. Health Education Research 1998;13:215‐24. - PubMed
-
- Jøsendal O, Aarø LE, Torsheim T, Rasbash. Evaluation of the school‐based smoking‐prevention program "Be smokeFree". Scandinavian Journal of Psychology 2005;46:189‐99. - PubMed
Olds 1998 {published data only}
-
- Olds DL, Henderson Jr CR, Cole R, Eckenrode J, Kitzman H, Luckey D, et al. Long‐term effects of nurse home visitation on children's criminal and antisocial behavior: 15‐year follow‐up of a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1998;280(14):1238‐44. - PubMed
Pierce 2008 {published and unpublished data}
Prado 2007 {published data only}
Reddy 2002 {published data only}
-
- Reddy KS, Arora M, Perry CL, Nair B, Kohli A, Lytle LA, et al. Tobacco and alcohol use outcomes of a school‐based intervention in New Delhi. American Journal of Health Behavior 2002;26(3):173‐81. - PubMed
Riesch 2012 {published data only}
Schinke 2004 {published data only}
Spoth 2001 {published data only}
-
- Guyll M, Spoth RL, Chao W, Wickrama KAS, Russell D. Family‐focused preventive interventions: Evaluating parental risk moderation of substance use trajectories. Journal of Family Psychology 2004;18(2):293‐301. - PubMed
-
- Spoth R, Redmond C, Shin C, Azevedo K. Brief family intervention effects on adolescent substance initiation: School‐level growth curve analyses 6 years following baseline. Journal of Counseling and Clinical Psychology 2004;72:535‐42. - PubMed
-
- Spoth R, Reyes ML, Redmond C, Shin C. Assessing a public health approach to delay onset and progression of adolescent substance use: Latent transition and log‐linear analyses of longitudinal family preventive intervention outcomes. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1999;67(5):619‐30. - PubMed
-
- Spoth RL, Redmond C, Shin C. Randomized trial of brief family interventions for general populations: adolescent substance use outcomes 4 years following baseline. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2001;69(4):627‐42. - PubMed
Spoth 2002 {published data only}
-
- Spoth RL, Redmond C, Trudeau L, Shin C. Longitudinal substance initiation outcomes for a universal preventive intervention combining family and school programs. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2002;16(2):129‐34. - PubMed
-
- Trudeau L, Spoth R, Lillehoj C, Redmond C, Wickrama KAS. Effects of a Preventive Intervention on Adolescent Substance Use Initiation, Expectancies, and Refusal Intentions. Prevention Science 2003;4(2):109‐122. - PubMed
Stevens 2002 {published data only}
-
- Jones DJ, Olson AL, Forehand R, Gaffney CA, Zens MS, Bau JJ. A family‐focused randomized controlled trial to prevent adolescent alcohol and tobacco use: The moderating roles of positive parenting and adolescent gender. Behavior Therapy 2005;36:347‐355.
-
- Stevens MM, Olson AL, Gaffney CA, Tosteson TD, Mott LA, Starr P. A pediatric, practice‐based, randomized trial of drinking and smoking prevention and bicycle helmet, gun, and seatbelt safety promotion. Pediatrics 2002;109(3):490‐7. - PubMed
Storr 2002 {published data only}
-
- Furr‐Holden CDM, Ialongo NS, Anthony JC, Petras H, Kellam SG. Developmentally inspired drug prevention: middle school outcomes in a school‐based randomized prevention trial. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2004;73:149‐58. - PubMed
-
- Ialongo N, Poduska J, Werthamer L, Kellam S. The distal impact of preventive interventions on conduct problems and disorder in early adolescence. Journal of Emotional Behavior Disorders 2001;9:146‐160.
-
- Ialongo NS, Werthamer L, Kellam SG. Proximal impact of two first‐grade preventive interventions on the early risk behaviors for later substance abuse, depression and antisocial behavior. American Journal of Community Psychology 1999;27(5):599‐641. - PubMed
-
- Storr CL, Ialongo NS, Kellam SG, Anthony JC. A randomized controlled trial of two primary school intervention strategies to prevent early onset tobacco smoking. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2002;66(1):51‐60. - PubMed
Wu 2003 {published data only}
-
- Stanton B, Cole M, Galbraith J, Li X, Pendleton S, Cottrel L, et al. Randomized trial of a parent intervention: parents can make a difference in long‐term adolescent risk behaviors, perceptions, and knowledge. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 2004;158:947‐55. - PubMed
-
- Wu Y, Stanton BF, Galbraith J, Kaljee L, Cottrell L, Li X. Sustaining and broadening intervention impact: a longitudinal randomized trial of 3 adolescent risk reduction approaches. Pediatrics 2003;111(1):e32‐e36. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abdullah 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Abdullah ASM, Lam TH, Mak YW, Loke AY. A randomized controlled trial of a smoking cessation intervention on parents of young children ‐ a preliminary report [POS2‐011]. Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco 10th Annual Meeting, Feb 18‐21, Phoenix Arizona. 2004.
-
- Abdullah ASM, Mak YW, Loke AY, Lam T‐H. Smoking cessation intervention in parents of young children: a randomised controlled trial. Addiction 2005;100:1731‐1740. - PubMed
Albrecht 2006 {published data only}
-
- Albrecht SA, Caruthers D, Patrick T, Reynolds M, Salamie D, Higgins LW, et al. A randomized controlled trial of a smoking cessation intervention for pregnant adolescents. Nursing Research 2006;55(6):402‐10. - PubMed
Allendorf 1985 {published data only}
-
- Allendorf S, Sunseri AJ, Cullinan J, Oman JK. Student heart health knowledge, smoking attitudes, and self‐ esteem. Journal of School Health 1985;55(5):196‐9. - PubMed
Ariza 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ariza C, Nebot M, Tomas Z, Gimenez E, Valmayor S, Tarilonte V, et al. Longitudinal effects of the European smoking prevention framework approach (ESFA) project in Spanish adolescents. European Journal of Public Health 2008;18(5):491‐497. - PubMed
Beatty 2008 {published data only}
-
- Beatty SE, Cross DS, Shaw TM. The impact of a parent‐directed intervention on parent‐child communication about tobacco and alcohol. Drug and Alcohol Review 2008;27(6):591‐601. - PubMed
Biglan 2000 {published data only}
Broning 2014 {published data only}
Brotman 2008 {published data only}
-
- Brotman LM, Gouley KK, Huang KY, Rosenfelt A, O'Neal C, Klein RG, et al. Preventive intervention for preschoolers at high risk for antisocial behavior: Long‐term effects on child physical aggression and parenting practices. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology 2008;37(2):386‐96. - PubMed
Byrnes 2010 {published data only}
Charlier 2009 {published data only}
-
- Charlier N. Glover M. Robertson J. Keeping Kids Smokefree: lessons learned on community participation. Health Education Research 2009;24(6):949‐56. - PubMed
Cohen 1989 {published data only}
-
- Cohen RY, Felix MR, Brownell KD. The role of parents and older peers in school‐based cardiovascular prevention programs: implications for program development. Health Education Quarterly 1989;16(2):245‐53. - PubMed
Cohen 1995 {published data only}
Cruz 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cruz GG, Ferrero MB, Coca IA, Maderuelo JA, García MT. Program for the prevention of smoking in secondary school students. Archivos de Bronconeumología 2009;45(1):16‐23. - PubMed
DeGarmo 2009 {published data only}
Eckenrode 2010 {published data only}
-
- Eckenrode J, Campa M, Luckey DW, Henderson CR, Cole R, Kitzman H, et al. Long‐term effects of prenatal and infancy nurse home visitation on the life course of youths: 19‐year follow‐up of a randomized trial. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2010;164:9‐15. - PubMed
Ellickson 2003 {published data only}
Faggiano 2008 {published data only}
-
- Faggiano F, Galanti MR, Bohrn K, Burkhart G, Vigna‐Taglianti F, Cuomo L, et al. The effectiveness of a school‐based substance abuse prevention program: EU‐Dap cluster randomized controlled trial. Preventive Medicine 2008;47:537‐543. - PubMed
-
- Faggiano F, Richardson C, Bohrn K, Galanti MR, EU‐Dap Study Group. A cluster randomized controlled trial of school‐based prevention of tobacco,alcohol and drug use: The EU‐Dap design and study population. Preventive Medicine 2007;44:170‐173. - PubMed
-
- Faggiano F, Vigna‐Tagliantia F, Burkhart G, Bohrn K, Cuomo L, Gregori D, et al. The effectiveness of a school‐based substance abuse prevention program:18‐Month follow‐up of the EU‐Dap cluster randomized controlled trial. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2010;108:56‐64. - PubMed
-
- Kreeft P, Wiborg G, Galanti MR, Siliquini R, Bohrn K, Scatigna M, et al. ‘Unplugged’: a new European school programme against substance abuse. Drugs: education, prevention and policy 2009;16(2):167‐181.
-
- Vigna‐Taglianti F, Vadrucci S, Faggiano F, Burkhart G, Siliquini R, Galanti MR. Is universal prevention against youths' substance misuse really universal? Gender‐specific effects in the EU‐Dap school‐based prevention trial. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 2009;63(9):722‐728. - PubMed
Flay 1988 {published data only}
-
- Flay BR, Brannon BR, Johnson CA, Hanson WB, Ulene AL, Whitney‐Saltiel DA, et al. The television school and family smoking prevention and cessation project. I. Theoretical basis and program development. Preventive Medicine 1988;17:585‐607. - PubMed
Glover 2009 {published data only}
-
- Glover M, Scragg R, Nosa V, Bullen C, McCool J, Kira A. Keeping Kids Smokefree: rationale, design, and implementation of a community, school, and family‐based intervention to modify behaviors related to smoking among Maori and Pacific Island children in New Zealand. International Quarterly of Community Health Education 2009‐2010;30(3):205‐222. - PubMed
Gordon 2008 {published data only}
Hahn 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hahn EJ, Hall LA, Rayens MK, Myers AV, Bonnel G. School‐ and home‐based drug prevention: Environmental, parent, and child risk reduction. Drugs: Education, Prevention and Policy 2007;14(4):319‐31.
Hansen 1987 {published data only}
-
- Hansen WB, Malotte CK, Fielding JE. Tobacco and alcohol prevention: Preliminary results of a four‐year study. Adolescent Psychiatry 1987;14:556‐75. - PubMed
Hansen 1991 {published data only}
-
- Hansen WB, Graham JW. Preventing alcohol, marijuana, and cigarette use among adolescents: peer pressure resistance training versus establishing conservative norms. Preventive Medicine 1991;20(3):414‐30. - PubMed
Hawkins 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hawkins J, Catalano R, Kosterman R, Abbott R, Hill KG. Preventing adolescent health‐risk behaviors by strengthening protection during childhood. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 1999;153(3):226‐34. - PubMed
Hawkins 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hawkins JD, Oesterle S, Brown EC, Monahan KC, Abbott RD, Arthur MW, et al. Sustained decreases in risk exposure and youth problem behaviors after installation of the Communities That Care prevention system in a randomized trial. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2012;166(2):141‐148. - PMC - PubMed
Horn 2007 {published data only}
-
- Horn K, Dino G, Hamilton C, Noerachmanto N. Efficacy of an emergency department‐based motivational teenage smoking intervention. Preventing Chronic Disease 2007;4(1):1‐12 www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2007/jan/06_0021.htm. - PMC - PubMed
Jackson 1994 {published data only}
-
- Jackson C, Bee‐Gates DJ, Henrisen L. Authoritative parenting, child competencies, and initiation of cigarette smoking. Health Education Quarterly 1994;21(1):103‐16. - PubMed
Johnson 1990 {published data only}
-
- Johnson CA, Pentz MA, Weber MD, Dwyer JH, Baer N, MacKinnon DP, et al. Relative effectiveness of comprehensive community programming for drug abuse prevention with high‐risk and low‐risk adolescents. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1990;58(4):447‐56. - PubMed
Jowers 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jowers KL, Bradshaw CP, Gately S. Taking school‐based substance abuse prevention to scale: District‐wide implementation of Keep A Clear Mind. Journal of Alcohol and Drug Education 2007;51(3):73‐91.
Knutsen 1991 {published data only}
-
- Knutsen SF, Knutsen R. The Tromso survey: The family intervention study ‐ the effect of intervention on some coronary risk factors and dietary habits, a 6‐year follow‐up. Preventive Medicine 1991;20(2):197‐212. - PubMed
Komro 2008 {published and unpublished data}
Kristjansson 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kristjansson AL, James JE, Allegrante JP, Sigfusdottir ID, Helgason AR. Adolescent substance use, parental monitoring, and leisure‐time activities: 12‐year outcomes of primary prevention in Iceland. Preventive Medicine 2010;51(2):168‐171. - PubMed
Krohn 1983 {published data only}
-
- Krohn MD, Massey JL, Skinner WF, Lauer RM. Social bonding theory and adolescent cigarette smoking: Longitudinal analysis. Journal of Health and Social Behavior 1983;24:337‐49. - PubMed
Kumpfer 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kumpfer XL, Xie J, O'Driscoll R. Effectiveness of a culturally adapted strengthening families program 12‐16 years for high risk Irish families. Child & Youth Care Forum 2012;41(2):173‐195.
Litrownik 2000 {published data only}
-
- Litrownik AJ, Elder JP, Campbell NR, Ayala GX, Slymen DJ, Parra MD, et al. Evaluation of a tobacco and alcohol use prevention program for Hispanic migrant adolescents: promoting the protective factor of parent‐child communication. Preventive Medicine 2000;31(2):124‐33. - PubMed
Lochman 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lochman JE, Wells KC. Contextual social‐cognitive mediators and child outcome: A test of the theoretical model in the Coping Power program. Developmental Psychopathology 2002;14:945‐67. - PubMed
-
- Lochman JE, Wells KC. Effectiveness of the Coping Power program and of classroom intervention with aggressive children. Behavior Therapy 2003;34:493‐515.
-
- Lochman JE, Wells KC. The Coping Power program for preadolescent aggressive boys and their parents. Outcome effects at the 1‐year follow‐up. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2004;72(4):571‐8. - PubMed
-
- Lochman JE, Wells KC. The Coping Power program in the middle‐school transition: Universal and indicated prevention effects. Psychology of Addictive Behavior 2002;16(4S):S40‐S54. - PubMed
Moncher 1994 {published data only}
-
- Moncher M, Schinke SP. Group intervention to prevent tobacco use among Native American youth. Special Issue: Empirical research on the outcomes of social work with groups. Research on Social Work Practice 1994;4(2):160‐71.
Nilsson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Nilsson M, Stenlund H, Bergström E, Weinehall L, Janlert U. It Takes Two: Reducing adolescent smoking uptake through sustainable adolescent–adult partnership. Journal of Adolescent Health 2006;39:880‐886. - PubMed
Nutbeam 1993 {published data only}
O'Byrne 2002 {published data only}
-
- O'Byrne KK, Haddock K, Poston WSC. Parenting style and adolescent smoking. Journal of Adolescent Health 2002;30:418‐25. - PubMed
Olds 2010 {published data only}
-
- Olds DL, Kitzman HJ, Cole RE, Hanks CA, Arcoleo KJ, Anson EA, et al. Enduring effects of prenatal and infancy home visiting by nurses on maternal life course and government spending: follow‐up of a randomized trial among children at age 12 years. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2010;164:419‐24. - PMC - PubMed
Parsai 2009 {published data only}
Patten 2006 {published data only}
-
- Patten CA, Croghan IT, Meis TM, Decker PA, Pingree S, Colligan RC, et al. Randomized clinical trial of an internet‐based versus brief office intervention for adolescent smoking cessation. Patient Education and Counseling 2006;64:249‐58. - PubMed
Pentz 1989 {published data only}
-
- Pentz MA, Johnson A, Dwyer JH, MacKinnon DM, Hansen WB, Flay BR. A comprehensive community approach to adolescent drug abuse prevention: effects on cardiovascular disease risk behaviors. Annals of Medicine 1989;21:219‐22. - PubMed
Pentz 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Pentz MA, Riggs NR. Longitudinal relationships of executive cognitive function and parent influence to child substance use and physical activity. Prevention Science 2013;14:229‐237. - PubMed
Perry 1990 {published data only}
-
- Perry CL, Pirie P, Holder W, Halper A, Dudovitz B. Parent involvement in cigarette smoking prevention: Two pilot evaluations of the "Unpuffables Program". Journal of School Health 1990;60(9):443‐7. - PubMed
Perry 2003 {published data only}
-
- Perry CL, Komro KA, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Bosma LM, Farbakhsh K, Munson KA, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the middle and junior high school D.A.R.E. and D.A.R.E. plus programs. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine 2003;157:178‐184. - PubMed
Perry 2009 {published data only}
Piper 2000 {published data only}
-
- Piper DL, Moberg P, King MJ. The HEALTHY FOR LIFE Project: behavioural outcomes. The Journal of Primary Prevention 2000;21(1):47‐73.
Ramchand 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ramchand R. Adolescent work experiences and drug involvement in an urban environment. Ph.D. Dissertation Johns Hopkins University 2006; Vol. UMI Microform 3213788.
Rohrbach 1994 {published data only}
-
- Rohrbach LA, Hodgson CS, Flay BR, Hansen WB, Pentz MA. Parental participation in drug abuse prevention: results from the Midwestern Prevention Project. Journal of Research on Adolescence 1994;4(2):295‐317.
Rohrbach 2002 {published data only}
Rosati 2012 {published data only}
Salminen 2005 {published data only}
-
- Salminen M, Vahlberg T, Ojanlatva A, Kivelä S‐L. Effects of a controlled family‐based health education/counseling intervention. American Journal of Health Behavior 2005;29(5):395‐406. - PubMed
Schinke 1988 {published data only}
Schinke 2000 {published data only}
-
- Schinke SP, Tepavac L, Cole KC. Preventing substance use among Native American youth: Three‐year results. Addictive Behaviors 2000;25(3):387‐97. - PubMed
Schinke 2009 {published data only}
Severson 1991 {published data only}
-
- Severson HH, Glasgow R, Wirt R, Brozovsky P, Zoref L, Black C, et al. Preventing the use of smokeless tobacco and cigarettes by teens; results of a classroom intervention. Health Education Research 1991;6(1):109‐20.
Simons‐Morton 2005 {published data only}
-
- Simons‐Morton B, Haynie D, Saylor K, Crump AD, Chen R. The effects of the Going Places program on early adolescent substance use and antisocial behavior. Prevention Science 2005;6(3):187‐197. - PubMed
Soper 2010 {published data only}
-
- Wolchik SA, Sandler IN, Millsap RE, Plummer B, Greene SM, Anderson ER, et al. Six‐year follow‐up of a randomized, controlled trial of preventive interventions for children of divorce. Journal of the American Medical Association 2002;28:1‐8. - PubMed
Spoth 2007 {published data only}
-
- Spoth R, Greenberg M, Bierman K, Redmond C. PROSPER community‐university partnership model for public education systems: capacity‐building for evidence‐based, competence‐building prevention. Prevention Science 2004;5:31‐9. - PubMed
Stevens 1993 {published data only}
-
- Stevens MM, Freeman DH, Mott LA, Youells FE, Linsey SC. Smokeless tobacco use among children: the New Hampshire study. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 1993;9:160‐6. - PubMed
Tang 1997 {published data only}
-
- Tang KC, Rissel C, Bauman A, Fay J, Porter S, Dawes A, et al. Evaluation of Kickbutts ‐ a school and community‐based smoking prevention program among a sample of year 7 and 8 students. Health Promotion Journal of Australia 1997;7:122‐7.
Tingen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tingen MS, Waller JL, Smith TM, Baker RR, Reyes J, Treiber FA. Tobacco prevention in children and cessation in family members. J Am Acad Nurse Practitioners 2006;18:169‐179. - PubMed
Vartiainen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Vartiainen E, Rennanen M, Kaukkala A, Dijk F, Lehtavuori R, Vries H. The effects of a three‐year smoking prevention programme in secondary schools in Helsinki. European Journal of Public Health 2007;17(3):249‐56. - PubMed
Vitória 2011 {published data only}
-
- Vitória, PD, Silva, SA, Vries H. Longitudinal evaluation of a smoking prevention program for adolescents [Avaliação longitudinal de programa de prevenção do tabagismo para adolescentes]. Revista Saúde Pública 2011;45(2):344‐354. - PubMed
Wakschlag 2011 {published data only}
Wen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wen XZ, Chen WQ, Lu CY, Liang CH, Zhang CX, Han K, et al. Process evaluation on a health promotion model regarding smoking prevention among Chinese secondary school students. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2007;28(3):224‐8. - PubMed
Werch 1991 {published data only}
-
- Werch CE, Young M, Clark M, Garrett C, Hooks S, Kersten C. Effects of a take‐home drug prevention program on drug‐related communication and beliefs of parents and children. Journal of School Health 1991;61(8):346‐50. - PubMed
-
- Young M, Kersten C, Werch C. Evaluation of a parent child drug education program. Journal of Drug Education 1996;26(1):57‐68. - PubMed
Werch 2005 {published data only}
-
- Werch C, Moore MJ, DiClemente CC, Bledsoe R, Jobli E. A multihealth intervention integrating physical activity and substance use prevention for adolescents. Prevention Science 2005;6(3):213‐226. - PubMed
Werch 2010 {published data only}
Wilson 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wilson DB, Jones RM, McClish D, Westerberg AL, Danish S. Fruit and vegetable intake among rural youth following a school‐based randomized controlled trial. Preventive Medicine 2012;54:150‐6. - PubMed
Wilson 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wilson IS, Ritchie D, Amos A, Shaw A, O'Donnell R, Mills LM, et al. 'I'm not doing this for me': mothers' accounts of creating smoke‐free homes. Health Education Research 2013;28(1):165‐78. - PubMed
Yilmaz 2013 {published data only}
-
- Yilmaz G, Caylan N, Karacan CD. Brief intervention to preteens and adolescents to create smoke‐free homes and cotinine results: a randomized trial. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2013;59(5):365‐71. - PubMed
Young 1996 {published data only}
-
- Young M, Kersten C, Werch C. Evaluation of a parent child drug education program. Journal of Drug Education 1996;26(1):49‐56. - PubMed
Zavela 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zavela KJ, Battistich V, Gosselink CA, Dean BJ. Say Yes First: Follow up of a five‐year rural drug prevention program. Journal of Drug Education 2004;34(1):73‐88. - PubMed
Additional references
Avenevoli 2003
-
- Avenevoli S, Merikangas KR. Familial influences on adolescent smoking. Addiction 2003;98 Suppl 1:1‐20. - PubMed
Baker 2015
Botvin 1993
-
- Botvin GJ, Baker E, Botvin EM, Dusenbury L, Cardwell J, Diaz T. Factors promoting cigarette smoking among Black youth: a causal modeling approach. Addictive Behaviors 1993;18:397‐405. - PubMed
Bricker 2003
-
- Bricker JB, Leroux BG, Petersen AV Jr, Kealey KA, Sarason IG, Anderson MR, et al. Nine‐year prospective relationship between parental smoking cessation and children's daily smoking. Addiction 2003;98:585‐93. - PubMed
Carson 2011
Carson 2012
Chassin 1984
-
- Chassin L, Presson CC. Predicting the onset of cigarette smoking in adolescents: A longitudinal study. Journal of Applied Social Psychology 1984;14(3):224‐43.
Chassin 1996
-
- Chassin L, Presson CC, Rose JS, Sherman SJ. The natural history of cigarette smoking from adolescence to adulthood: demographic predictors of continuity and change. Health Psychology 1996;15:478‐84. - PubMed
Covey 1990
Darling 2003
-
- Darling N, Cumsille P. Theory, measurement, and methods in the study of family influences on adolescent smoking. Addiction 2003;98 Suppl 1:21‐36. - PubMed
Dielman 1994
-
- Dielman TE. Correction for the design effect in school‐based substance use and abuse prevention research: Sample size requirements and analysis considerations. NIDA Research Monographs. Vol. 139, Washington, D.C: National Institute of Drug Addiction, 1994:115‐26. - PubMed
DuRant 1999
-
- DuRant RH, Smith JA, Kreiter SR, Krowchuk DP. The relationship between early age of onset of initial substance use and engaging in multiple health risk behaviors among young adolescents. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 1999;153(3):286‐91. - PubMed
Eisner 1989
-
- Eisner JR, Morgan M, Gammage P, Gray E. Adolescent smoking: Attitudes, norms and parental influence. British Journal of Social Psychology 1989;28:193‐202. - PubMed
Hussey 1992
-
- Hussey JM, Gilchrist LD, Gillmore MR, Lohr MR. Factors related to cigarette smoking during adolescent pregnancy. Journal of Youth and Adolescence 1992;21(4):409‐20. - PubMed
Huver 2007
-
- Huver RME, Engels RCME, Vries H. Are anti‐smoking parenting practices related to adolescent smoking cognitions and behavior?. Health Education Research 2007;21(1):66‐77. - PubMed
Isohanni 1991
-
- Isohanni M, Moilanen I, Rantakallio P. Determinants of teenage smoking, with reference to non‐standard family background. British Journal of Addictions 1991;86:391‐8. - PubMed
Jackson 1998
-
- Jackson C, Henriksen L, Foshee VA. The authoritative parenting index: predicting health risk behaviors among children and adolescents. Health Education & Behavior 1998;25(3):319‐37. - PubMed
Jarvis 1997
-
- Jarvis MJ. Patterns and predictors of smoking cessation in the general population. In: Bolliger CT, Fagerstroem KT editor(s). The tobacco epidemic. Progress in respiratory research no. 28. Basel: Karger, 1997:151‐64.
Johnston 2000
-
- Johnston LD, O'Malley PM, Bachman JG. The monitoring the future national survey results on adolescent drug use: overview of key findings, 1999. NIH Publ No. 00‐4690. Rockville, MD: National Institute of Drug Abuse, 2000:48. [NIH Publ No. 00‐4690]
Krosnick 1982
-
- Krosnick JA, Judd CM. Transitions in social influence at adolescence: Who induces cigarette smoking?. Developmental Psychology 1982;18(1):359‐68.
Mayhew 2000
-
- Mayhew KP, Flay BR, Mott JA. Stages in the development of adolescent smoking. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2000;59 Suppl 1:61‐81. - PubMed
Mounts 2002
-
- Mounts NS. Parental management of adolescent peer relationships in context: the role of parenting style. Journal of Family Psychology 2002;16:58‐69. - PubMed
Murray 1990
-
- Murray DM, Hannan PJ. Planning for the appropriate analysis in school‐based drug‐use prevention studies. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1990;58(4):458‐68. - PubMed
Murray 1997
-
- Murray DM, Short BJ. Intraclass correlation among measures related to tobacco use by adolescents: Estimates, correlates, and applications in intervention studies. Addictive Behaviors 1997;22(1):1‐12. - PubMed
Newman 1989
-
- Newman IM, Ward JM. The influence of parental attitude and behavior on early adolescent cigarette smoking. Journal of School Health 1989;59(4):150‐2. - PubMed
Palmer 1998
-
- Palmer RF, Graham JW, White EL, Hansen WB. Applying multilevel analytic strategies in adolescent substance use prevention research. Preventive Medicine 1998;27:328‐36. - PubMed
Patnode 2012
-
- Patnode CD, O'Connor E, Whitlock EP, Perdue LA, Soh C. Primary Care Relevant Interventions for Tobacco Use Prevention and Cessation in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Rockville, MD, USA: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (Internet File) December 2012. - PubMed
Petrie 2007
-
- Petrie J, Bunn F, Byrne G. Parenting programmes for preventing tobacco, alcohol or drugs misuse in children <18: a systematic review. Health Education Research 2007;22(2):177‐91. - PubMed
Proescholdbell 2000
-
- Proescholdbell RJ, Chassin L, MacKinnon DP. Home smoking restrictions and adolescent smoking. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2000;2(2):159‐67. - PubMed
Simons‐Morton 2002
-
- Simons‐Morton BG. Prospective analysis of peer and parent influences on smoking initiation among early adolescents. Prevention Science 2002;3:275‐83. - PubMed
Thomas 2011
Thomas 2013
Turner 1991
-
- Turner RA, Irwin JE Jr. Family structure, family processes, and experimenting with substances during adolescence. Journal of Research in Adolescence 1991;1:93‐106.
Tyas 1998
USDHHS 1994
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Report of the Surgeon General.. Preventing tobacco use among young people: a report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health, 1994.
References to other published versions of this review
Thomas 2003
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

